- 50 days free returns
- Rated “Great” on Trustpilot
- The UK's largest selection of brands
Extra 11% off over £99 & 14% off over £149
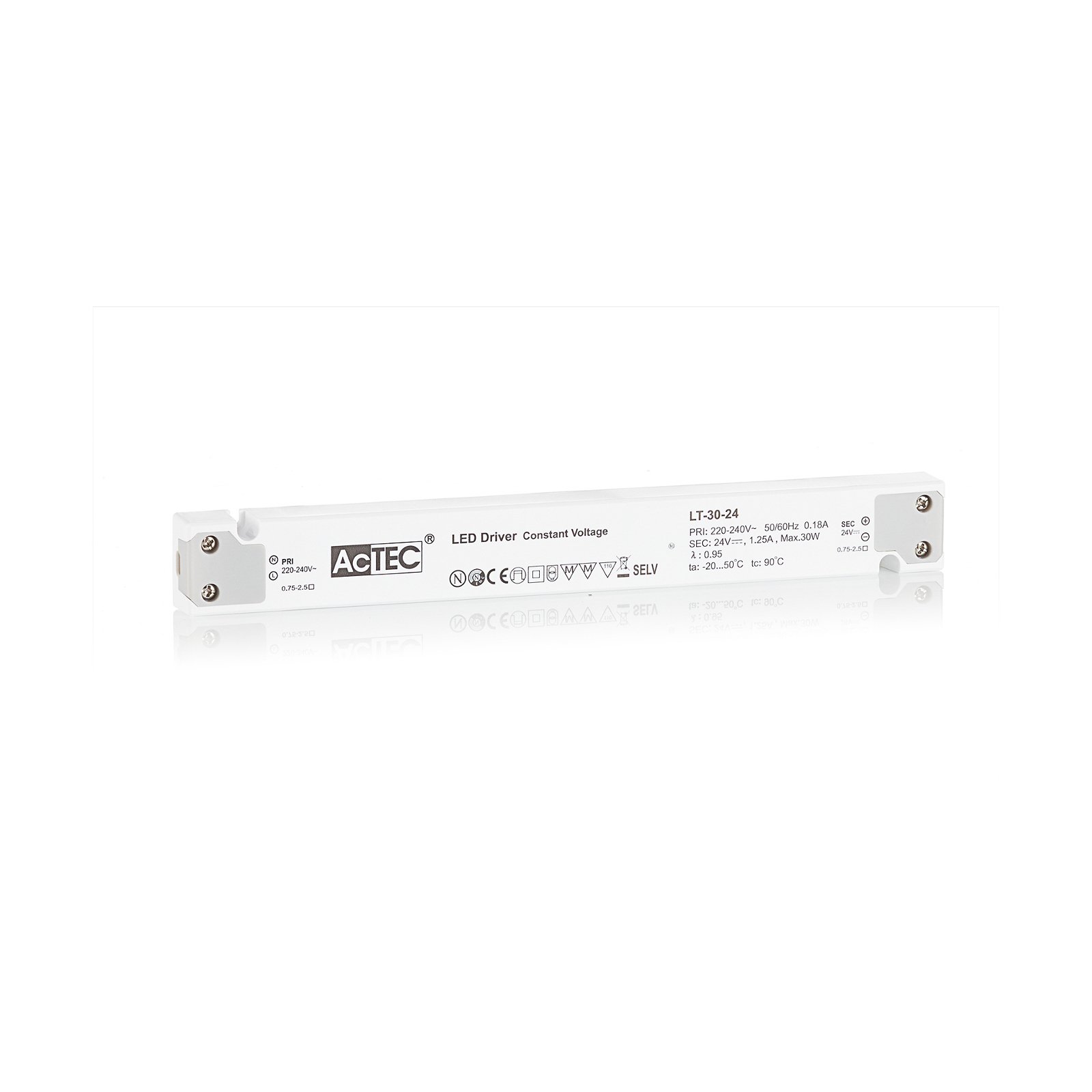
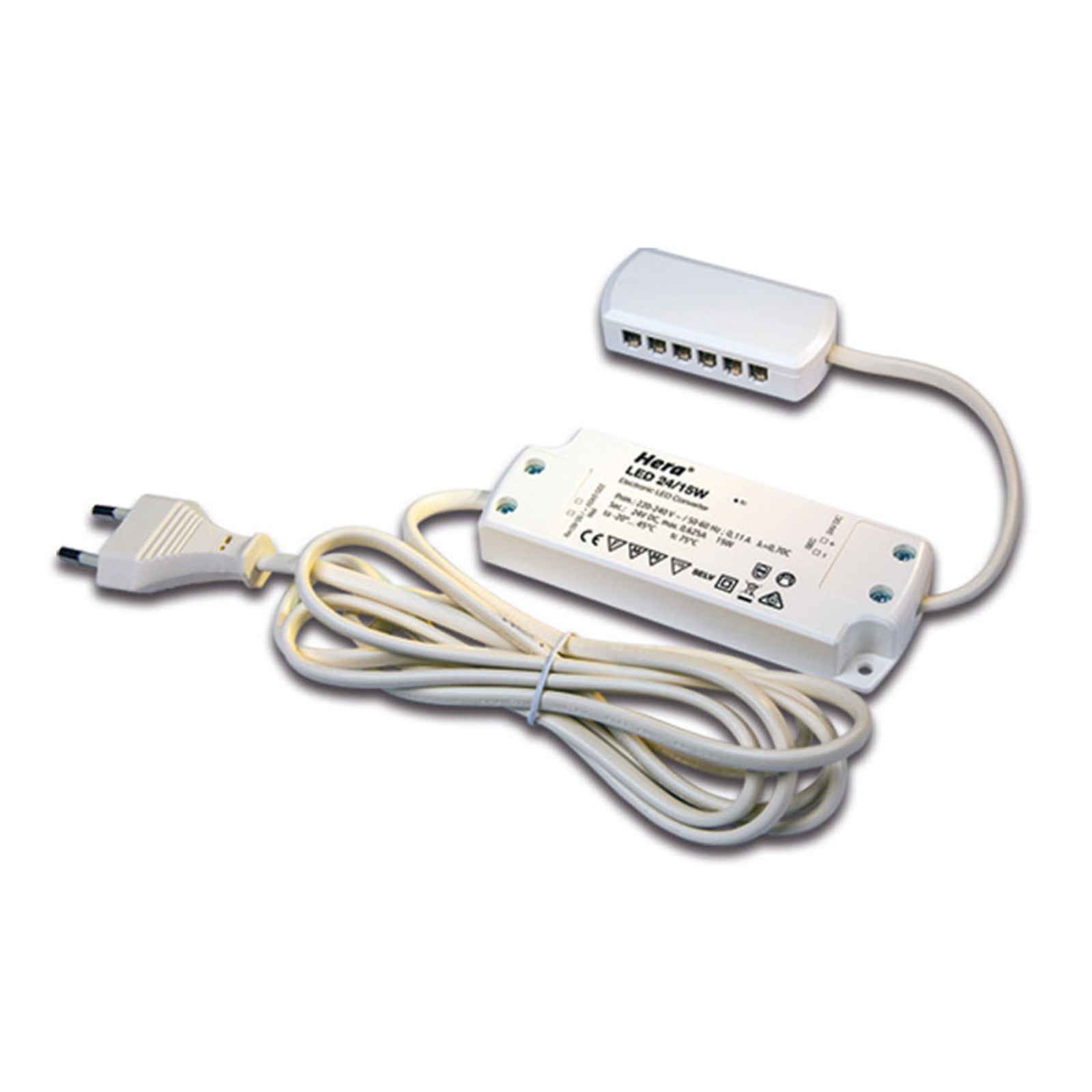
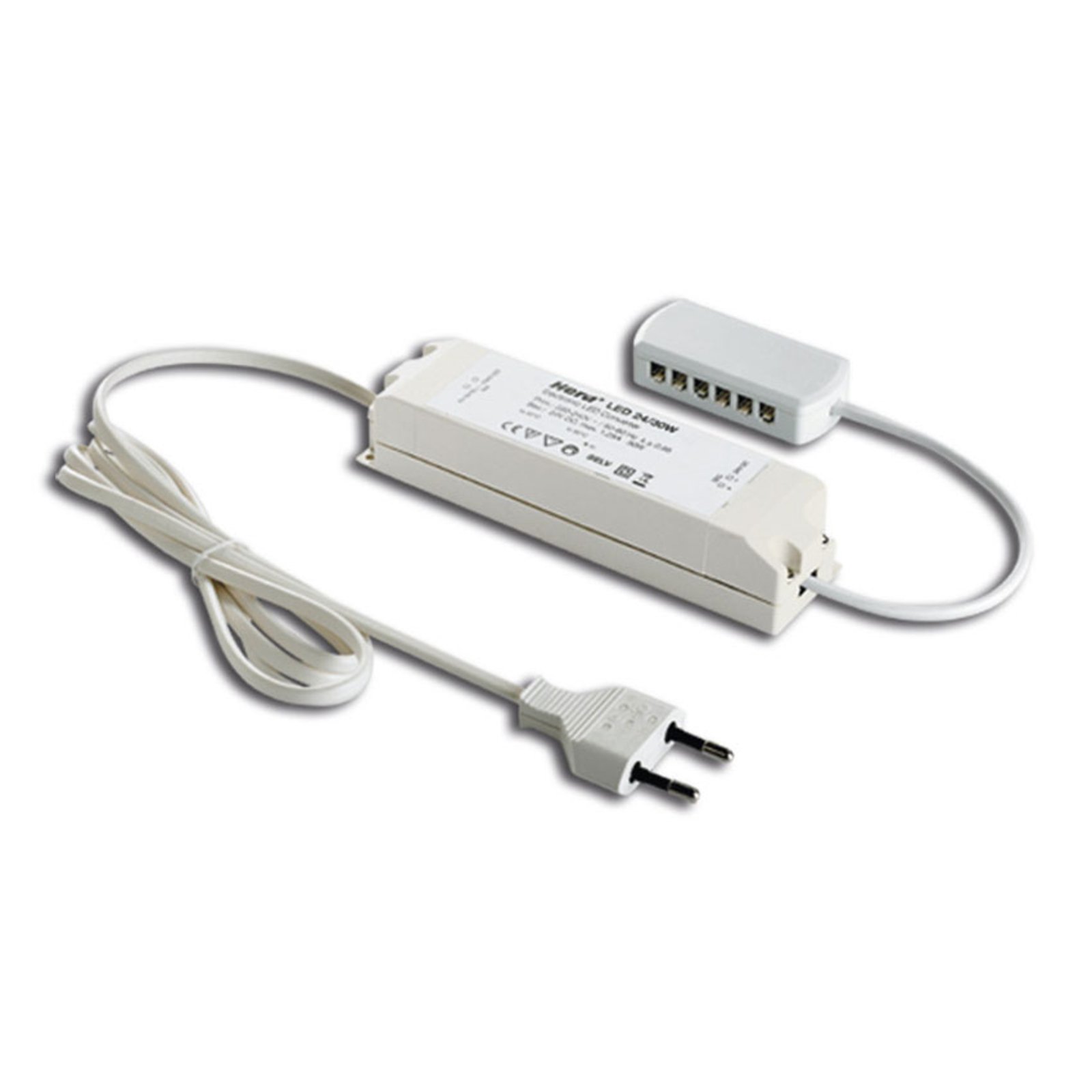
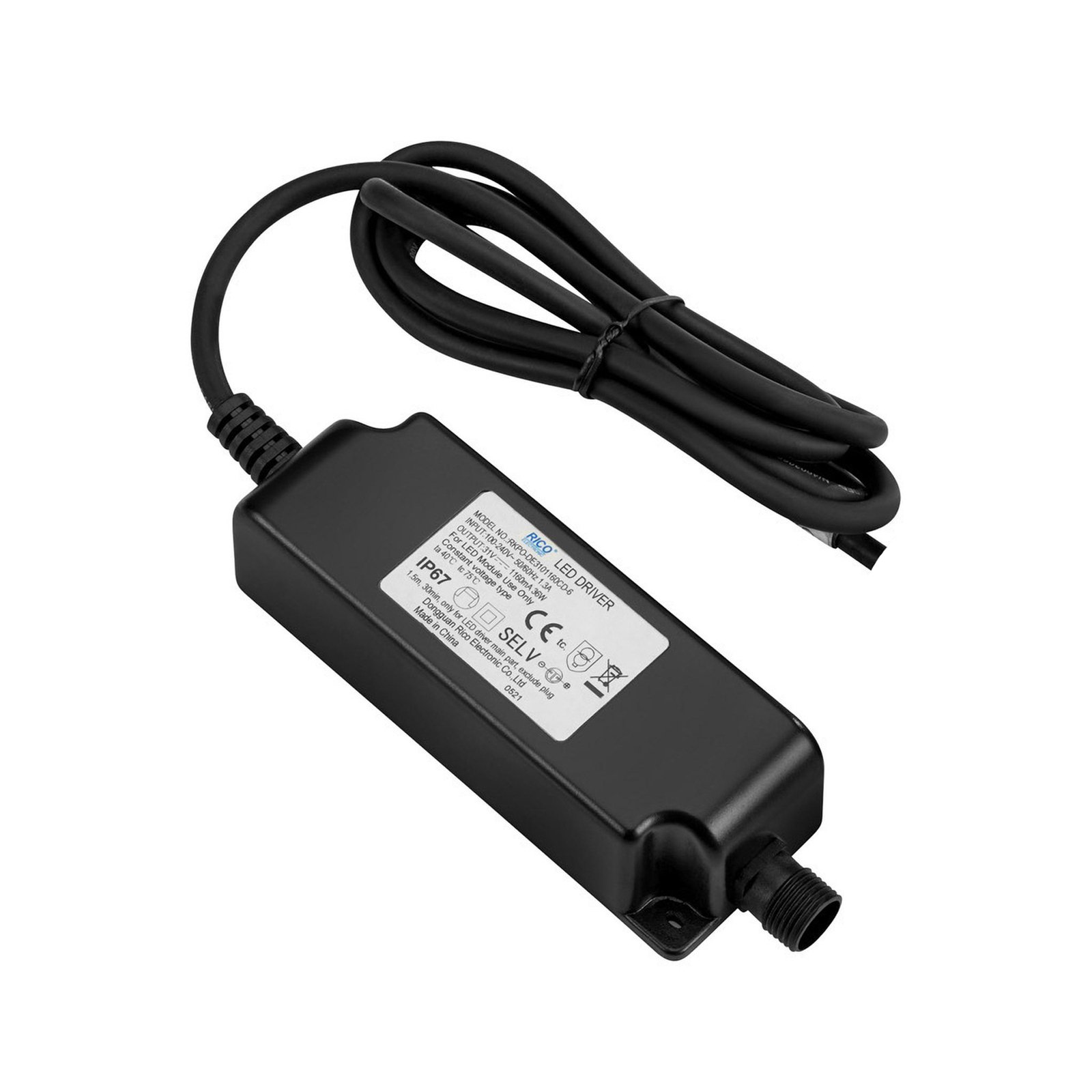
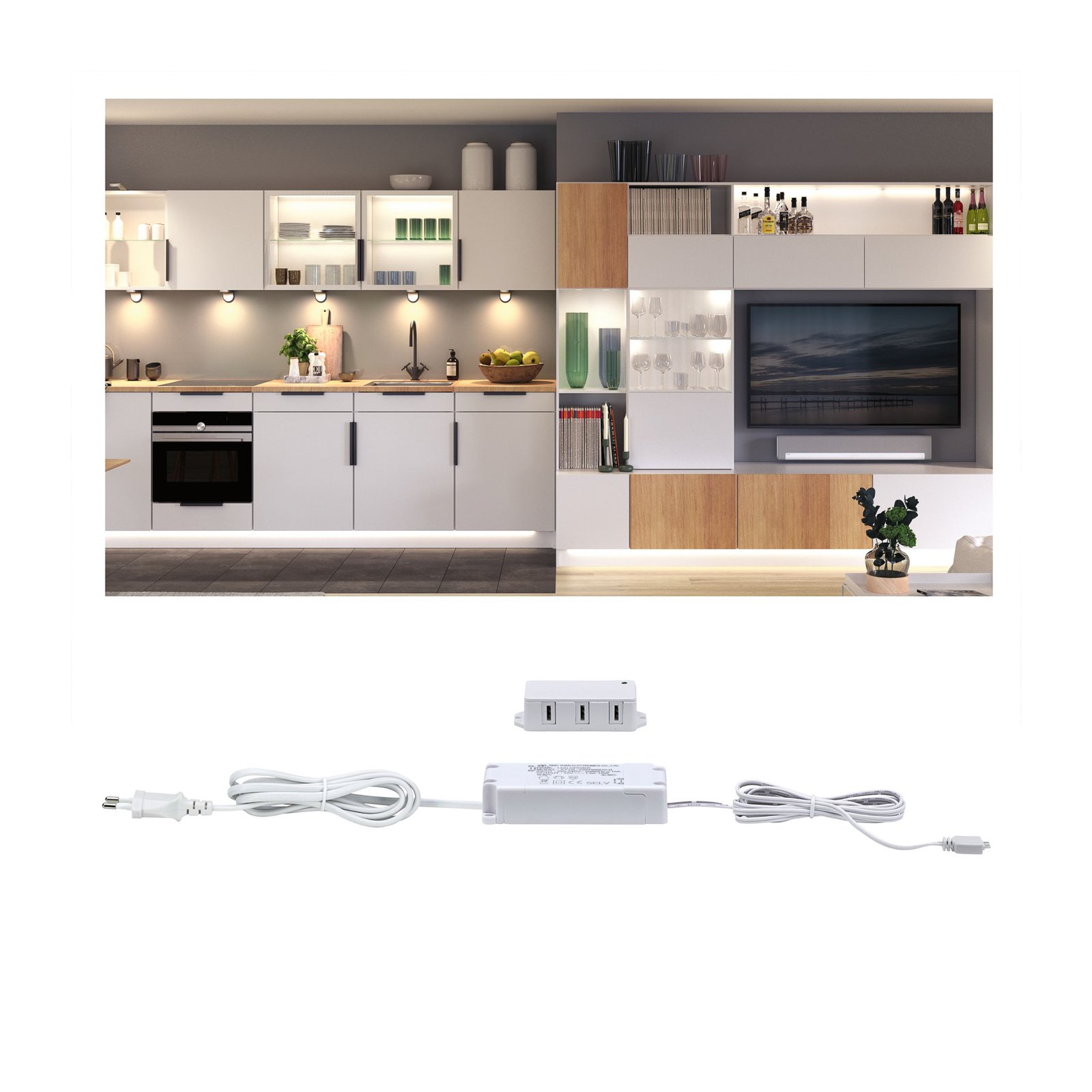
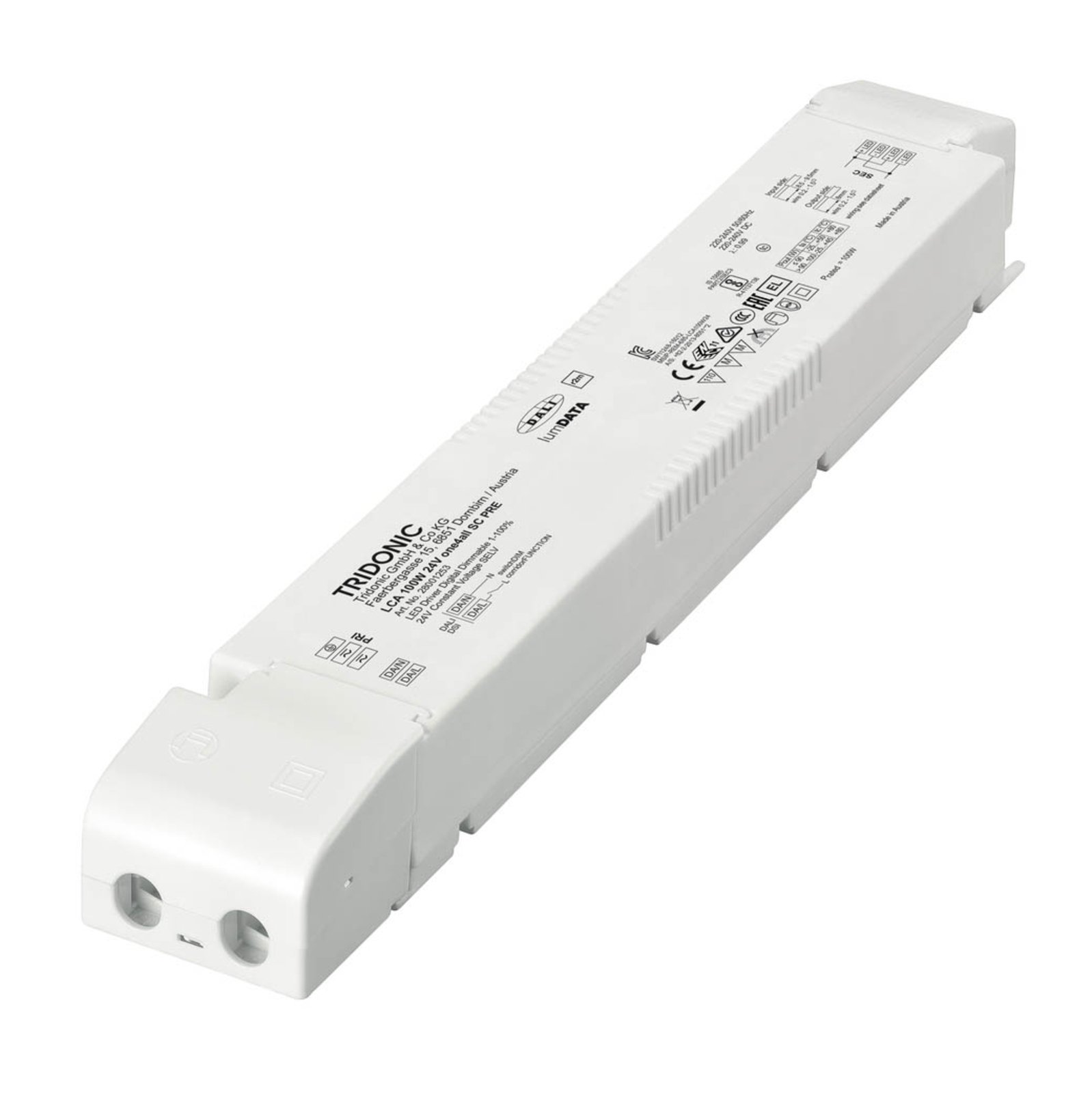
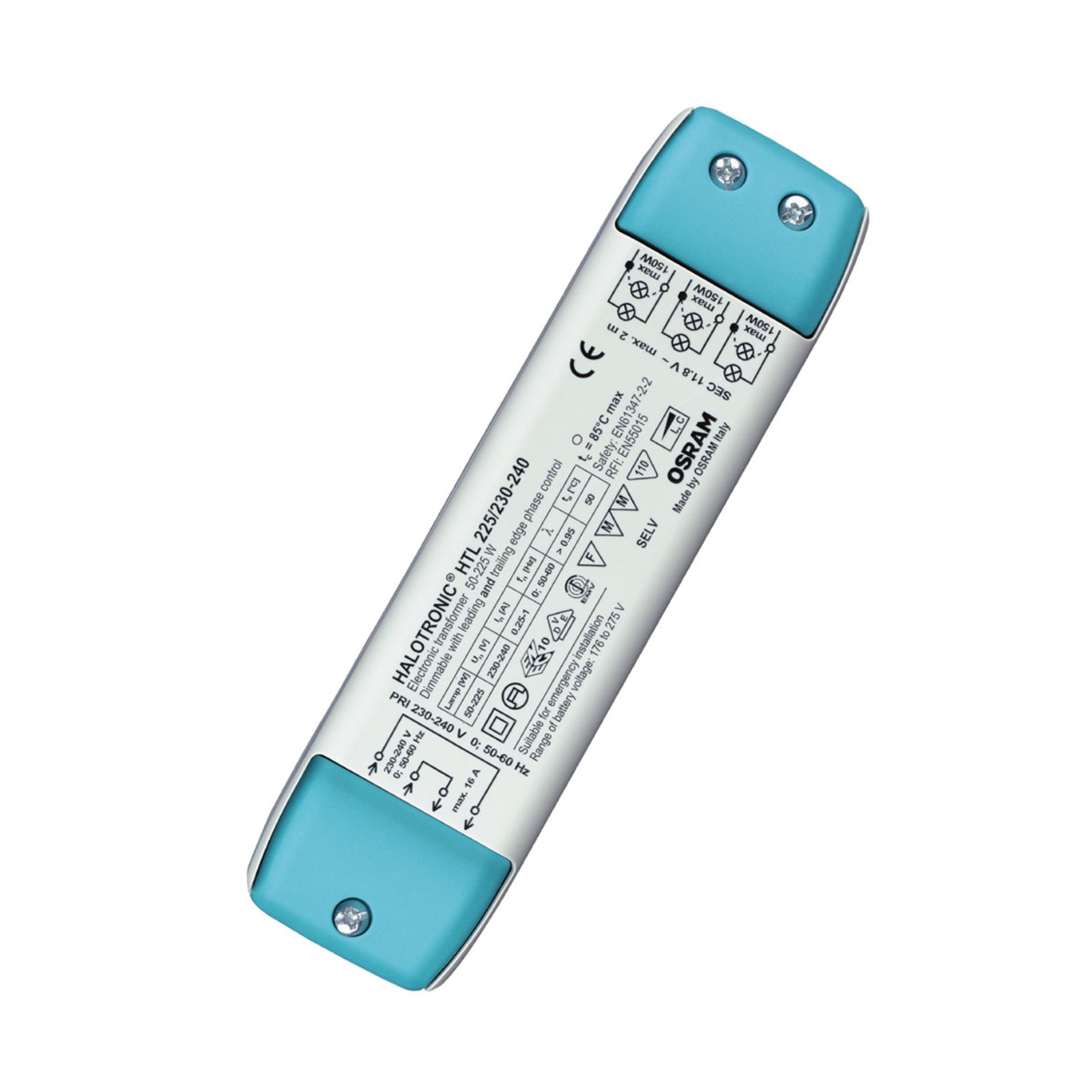
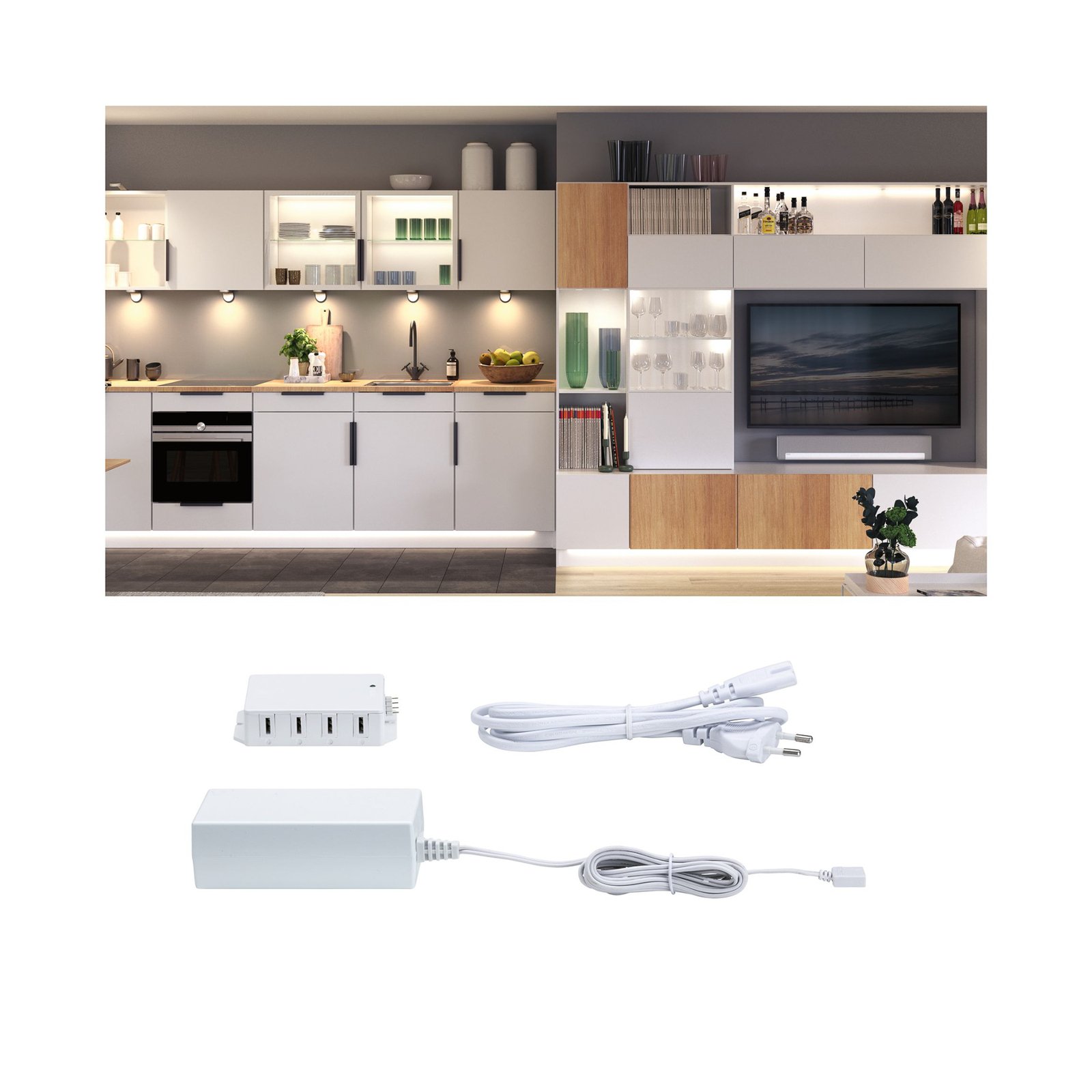
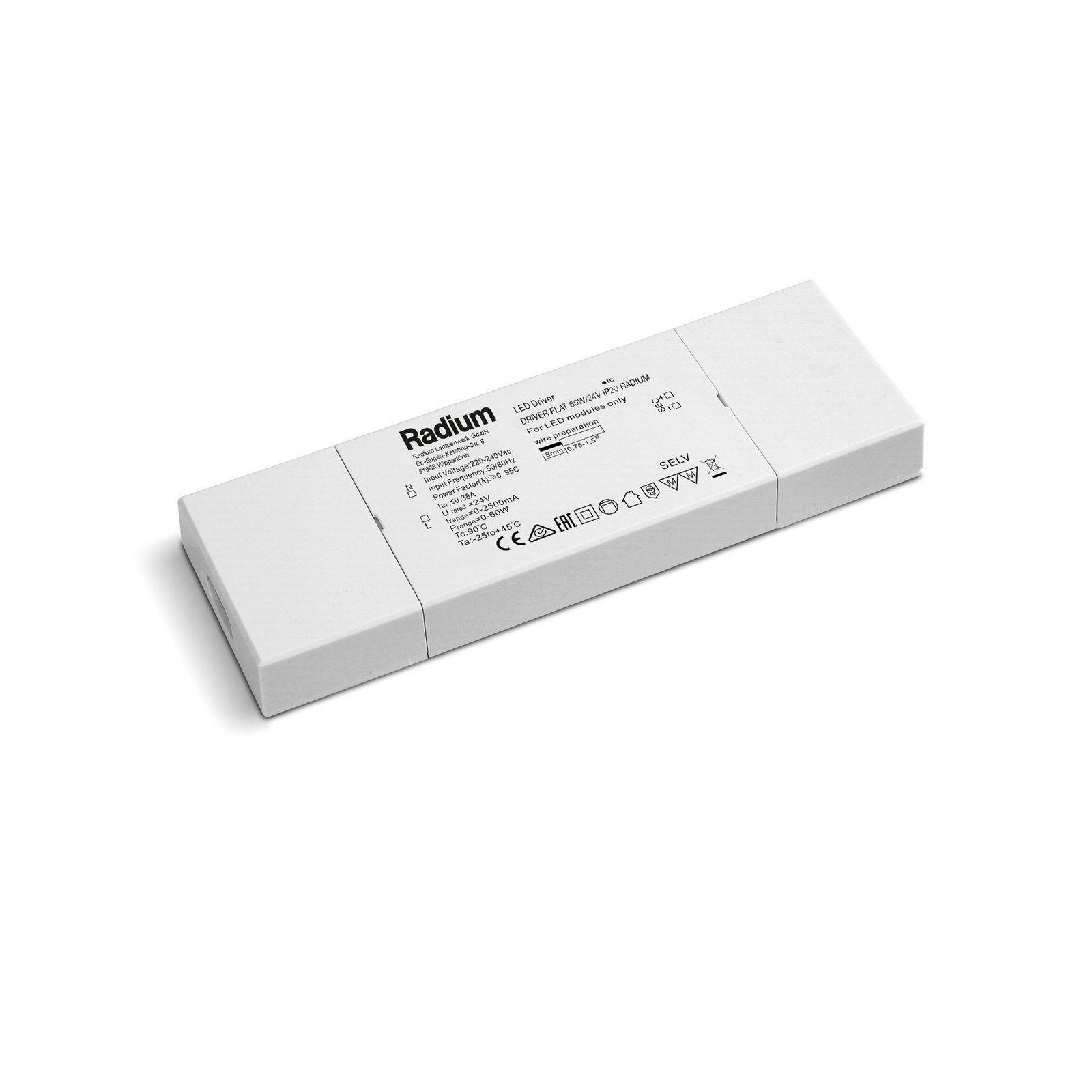
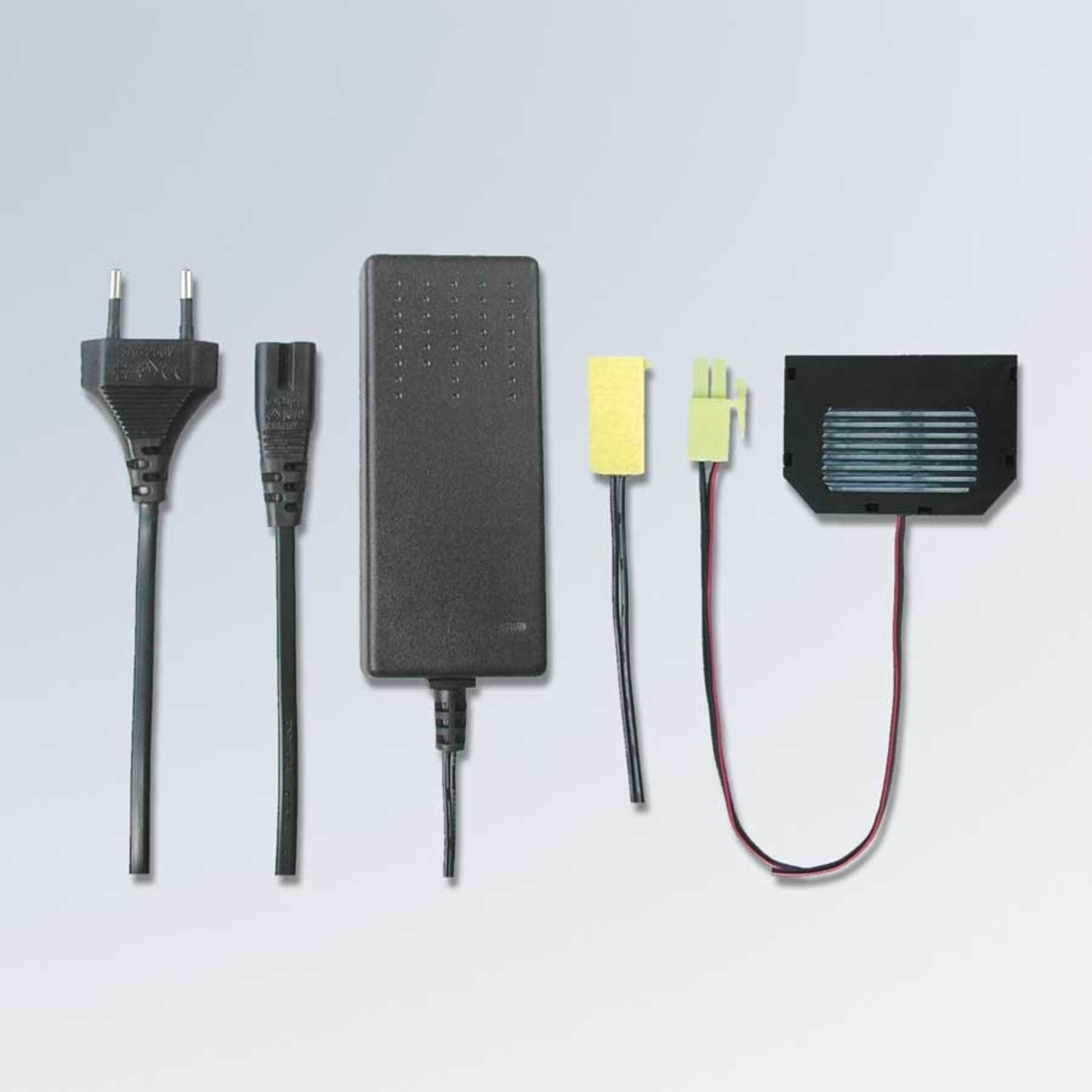
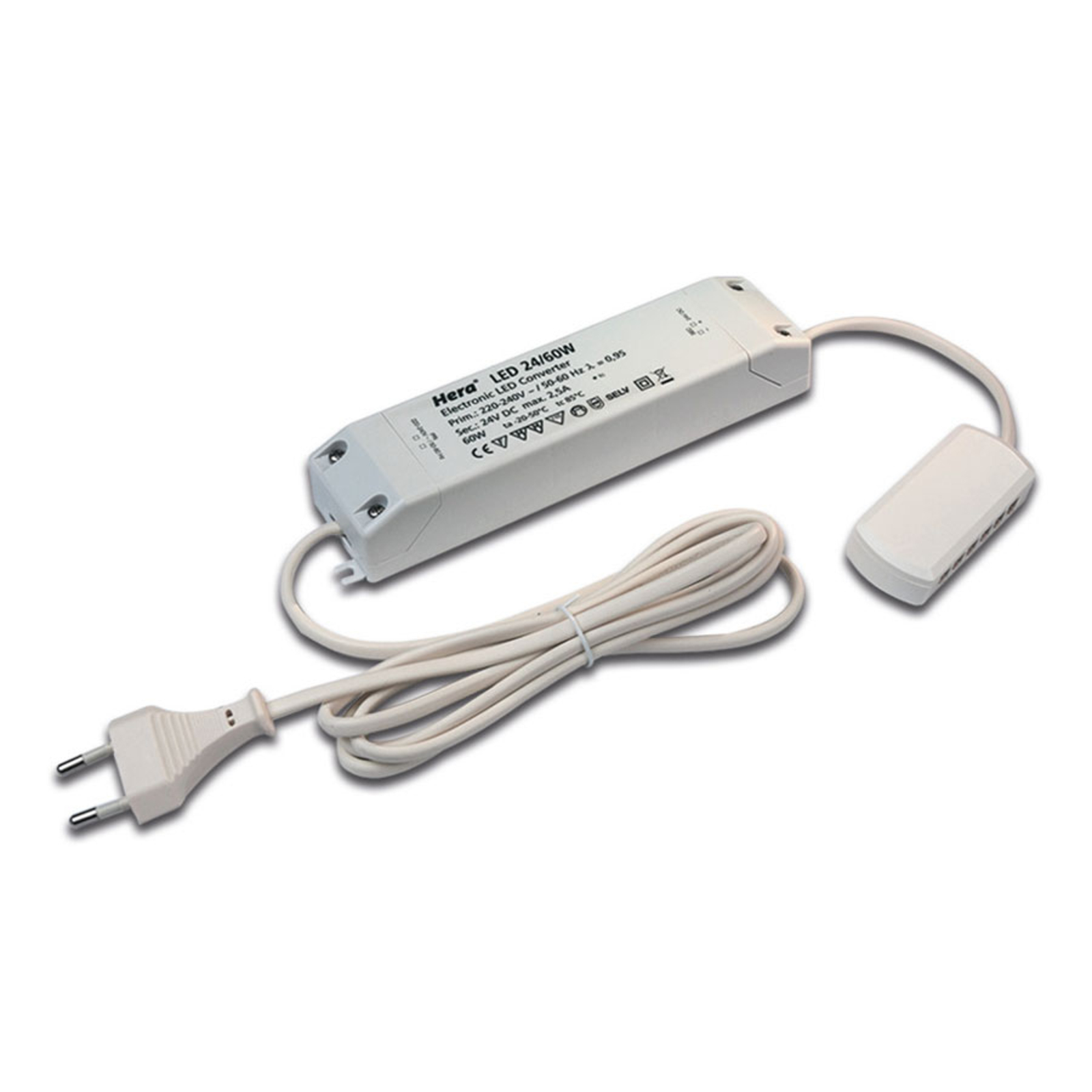
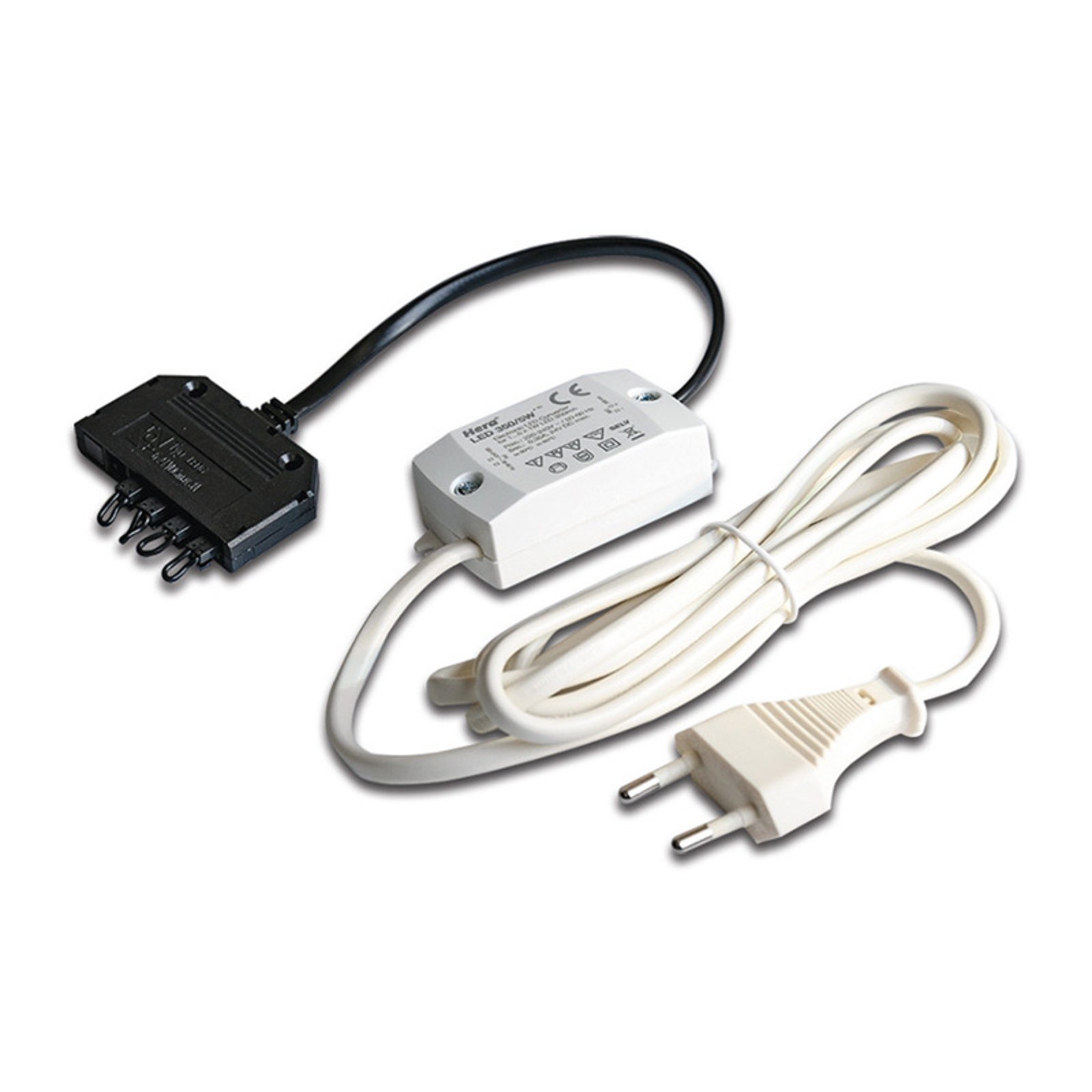
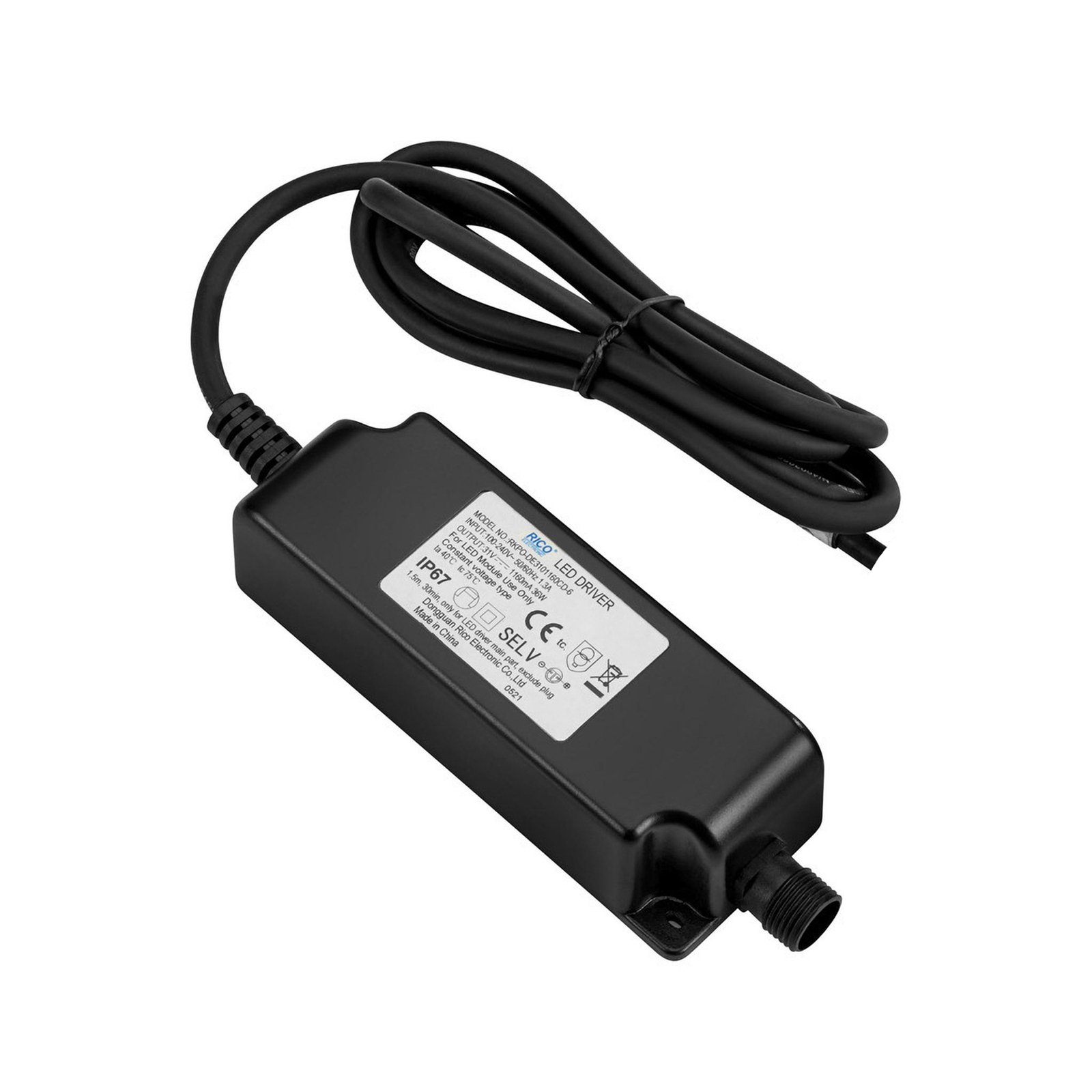
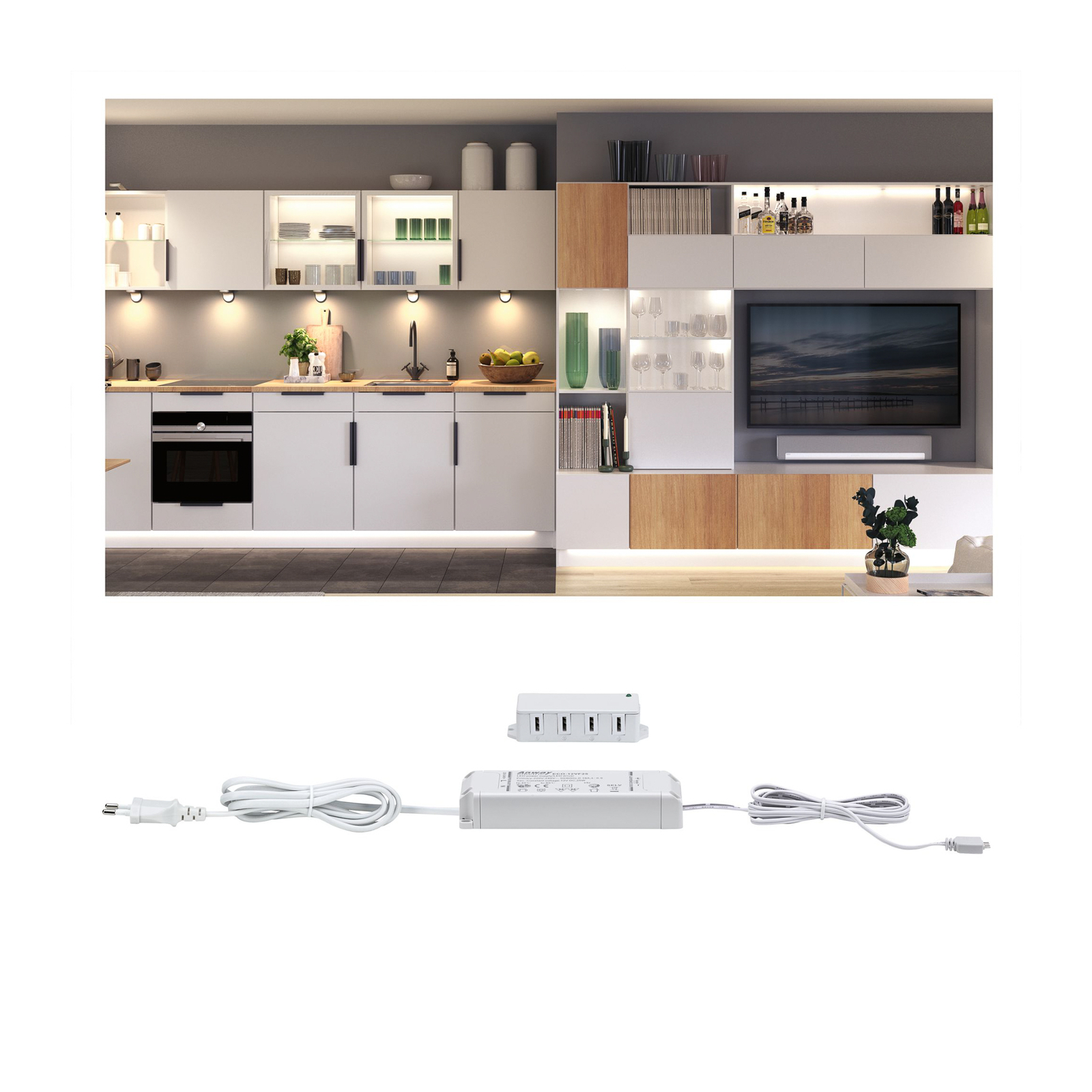
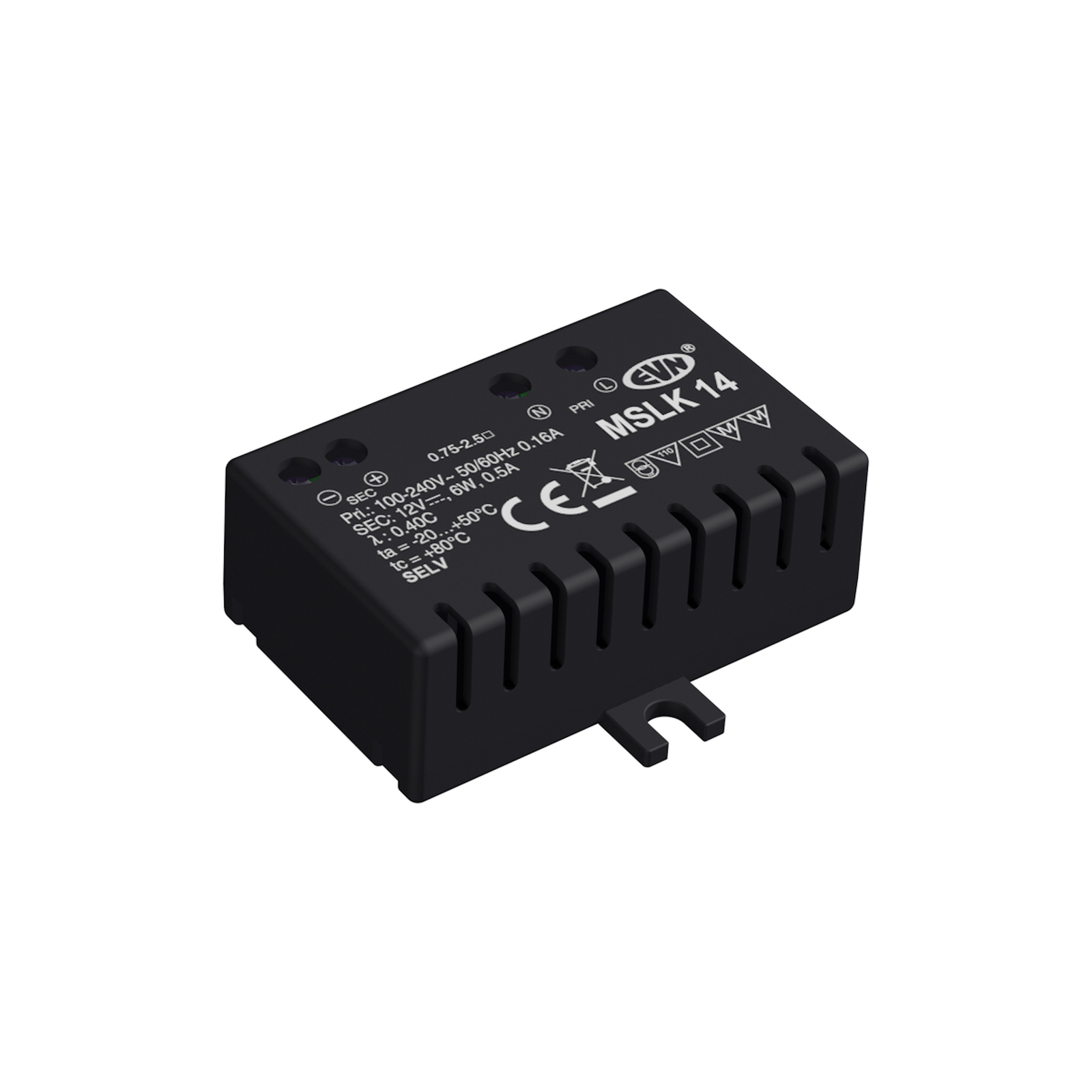
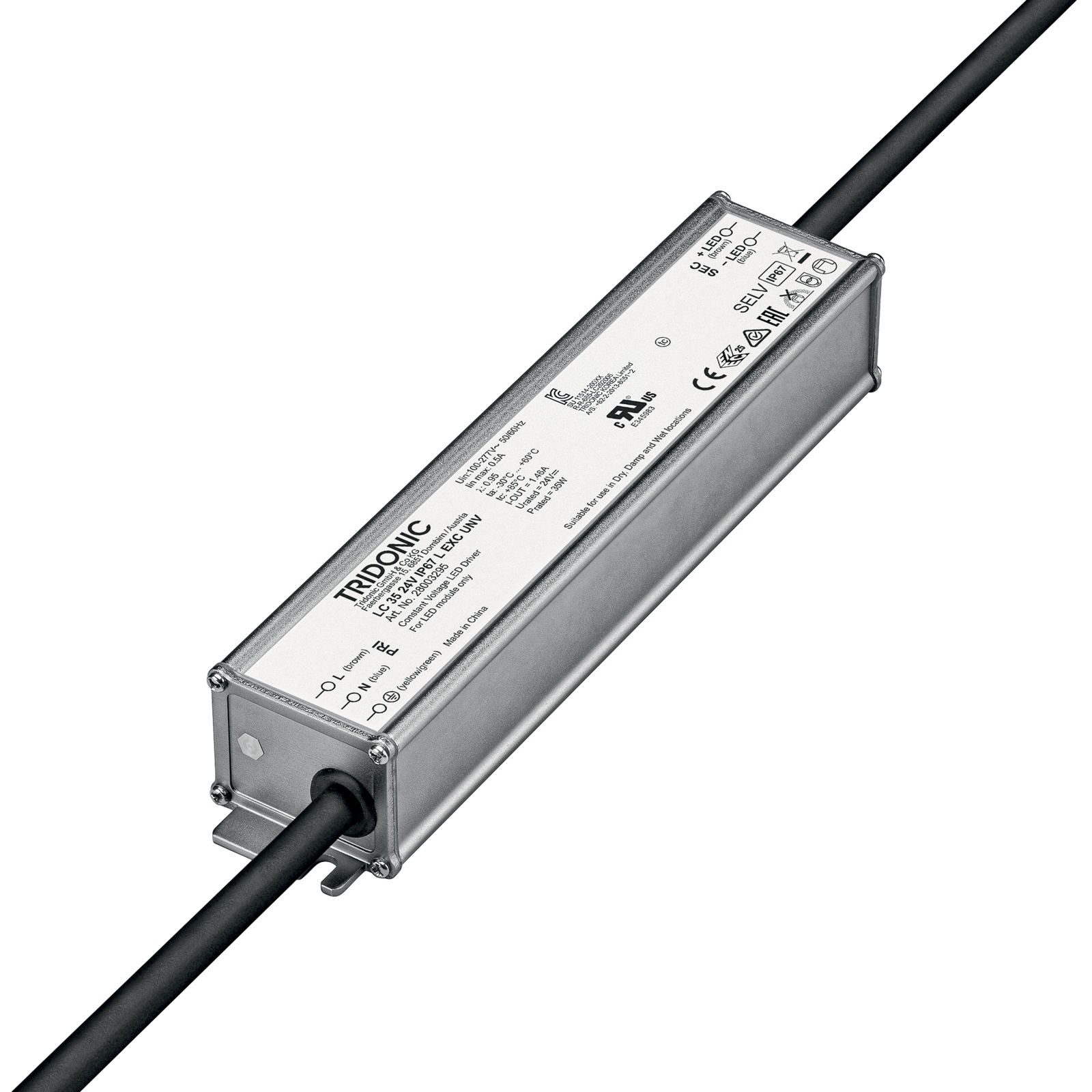
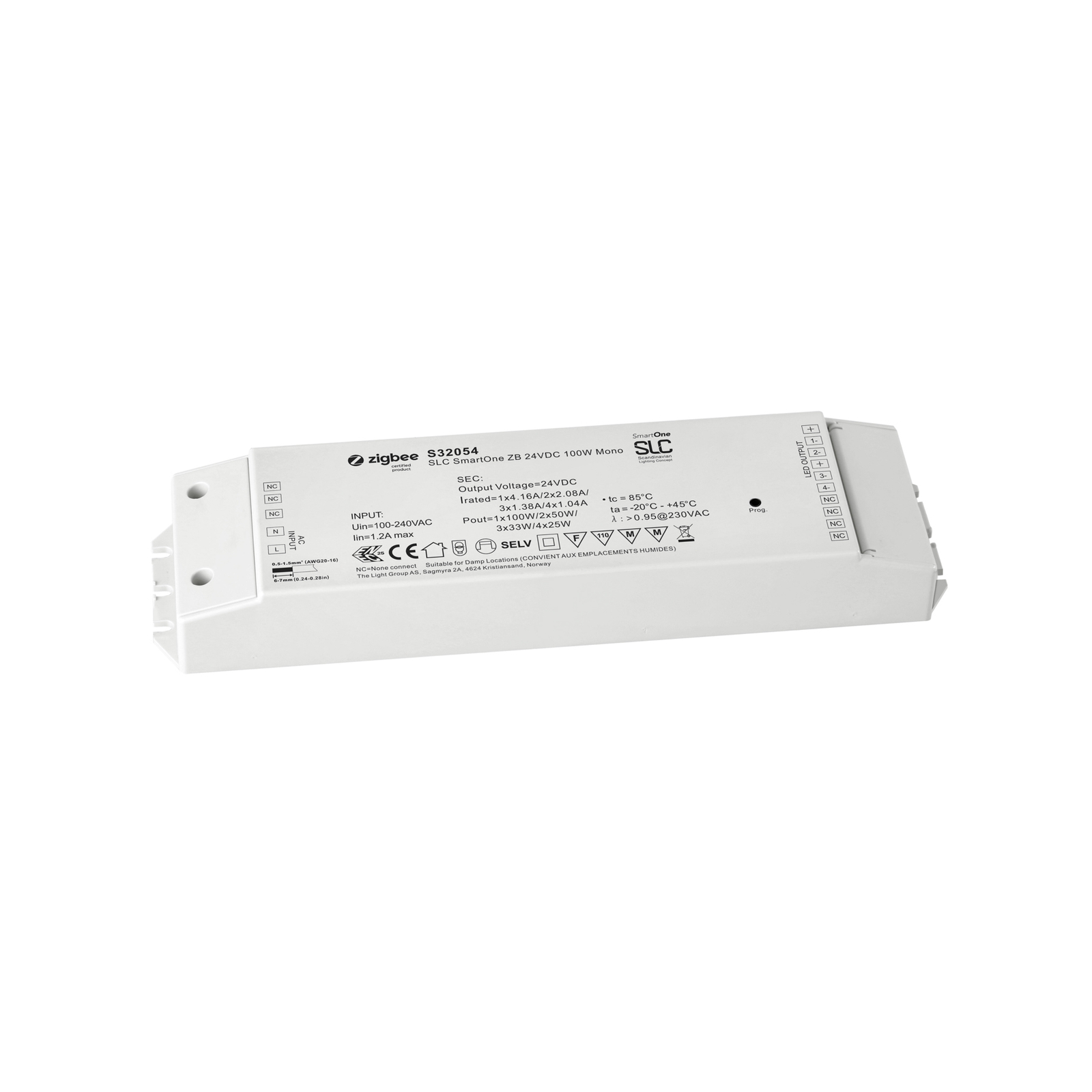
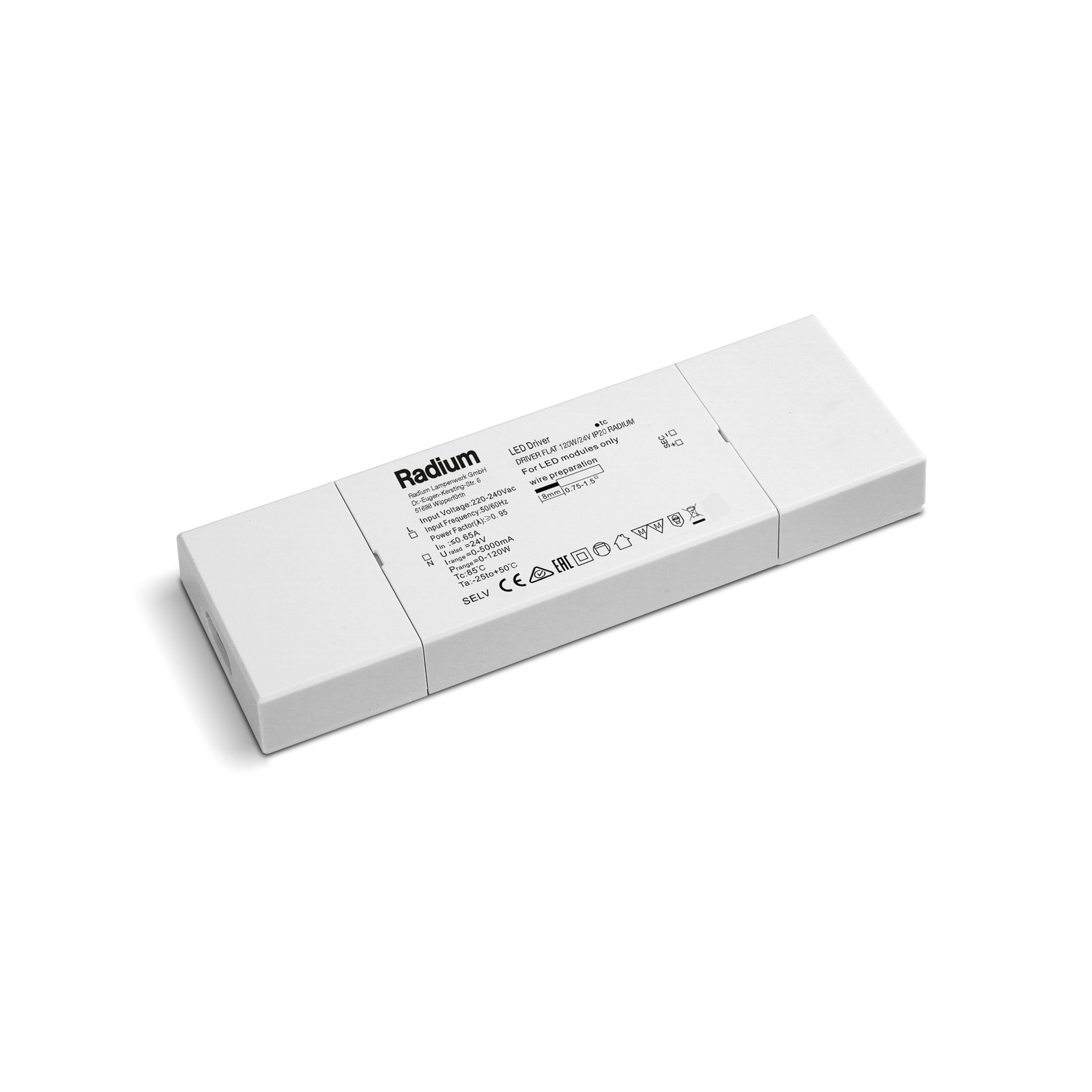
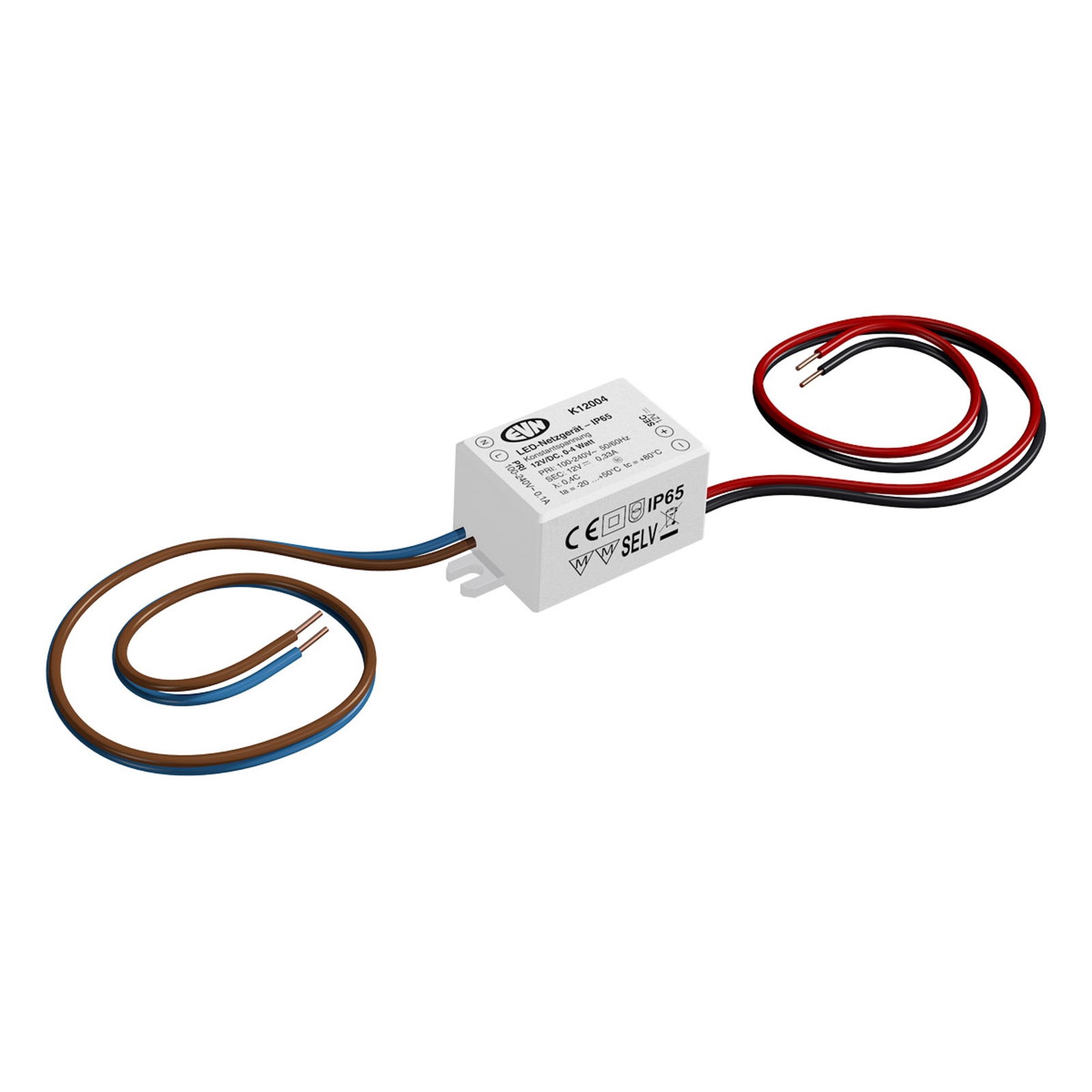
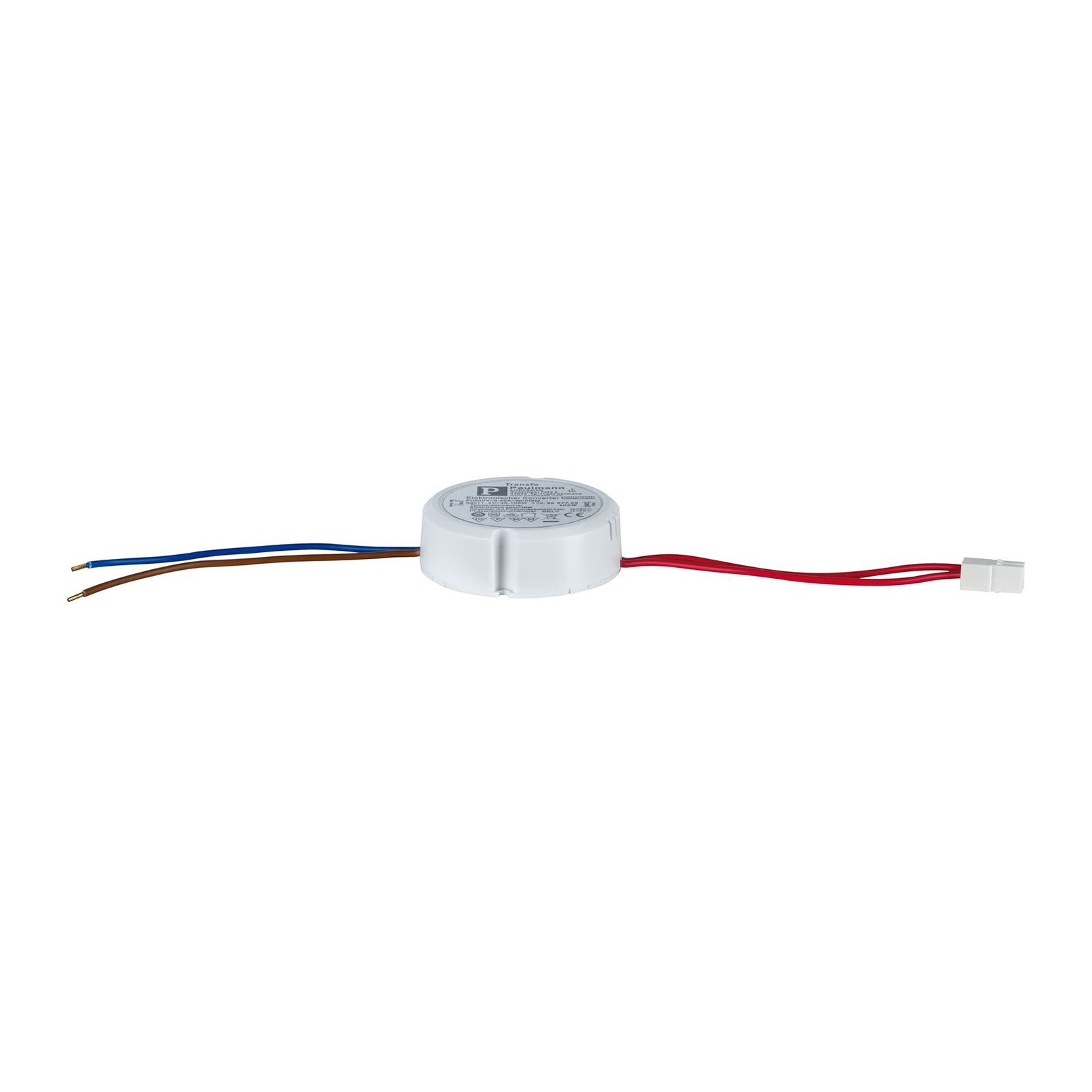
Transformers - the voltage transformers
Transformers, or transformers for short, convert our mains voltage of 230V into extra-low voltages of 6, 12 or 24V. They can also be translated as voltage transformers (Latin transformare = to transform, convert). In lighting technology, transformers are required for luminaires that are operated with low-voltage light sources. In general, transformers are an integral part of electrical engineering. They are responsible for reducing and increasing AC voltage and are found in almost all electrical appliances whose operating voltage differs from the mains voltage. Transformers are also indispensable in the general power supply, as electricity can only really be transported effectively using high-voltage lines and must therefore be converted again afterwards using a transformer.
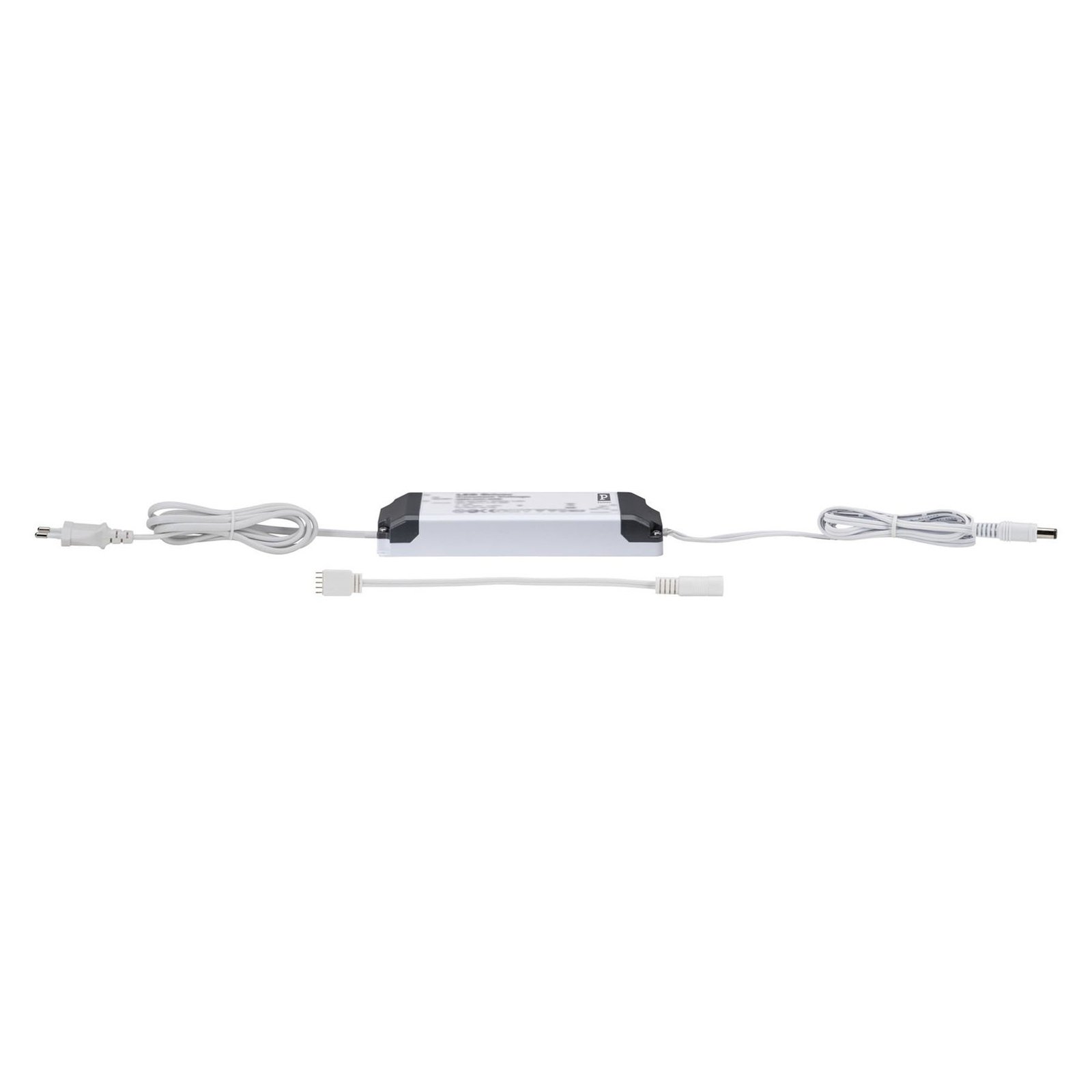
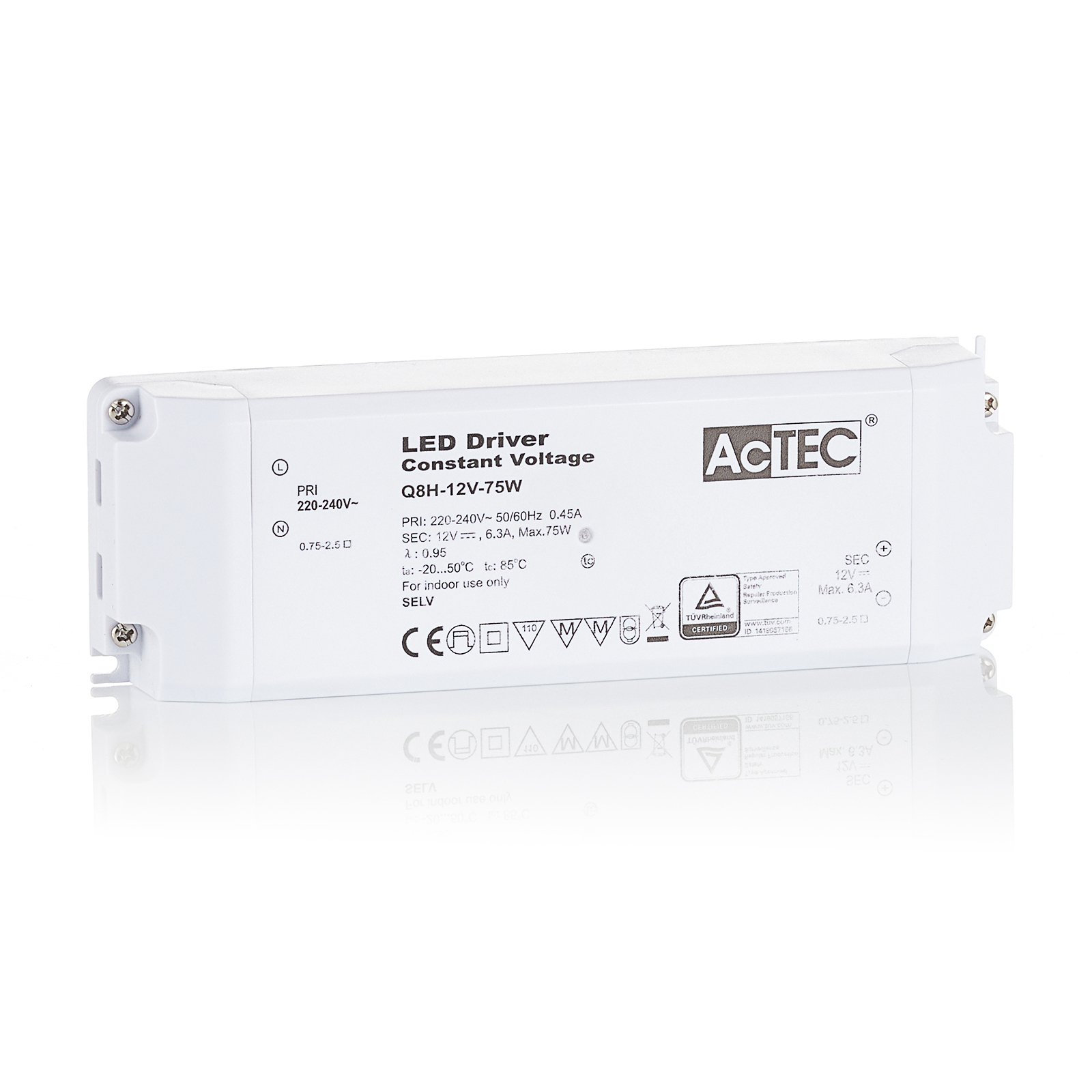
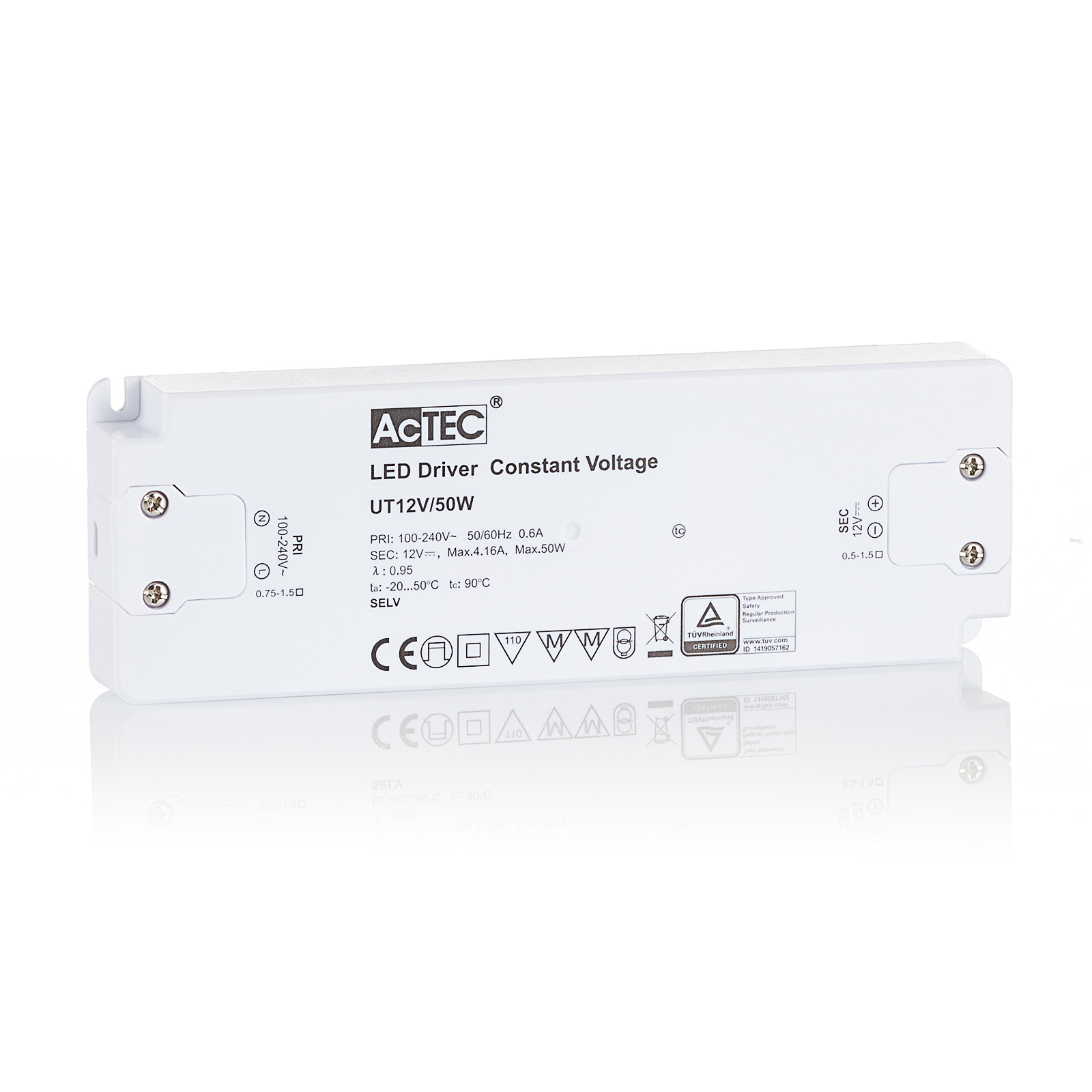
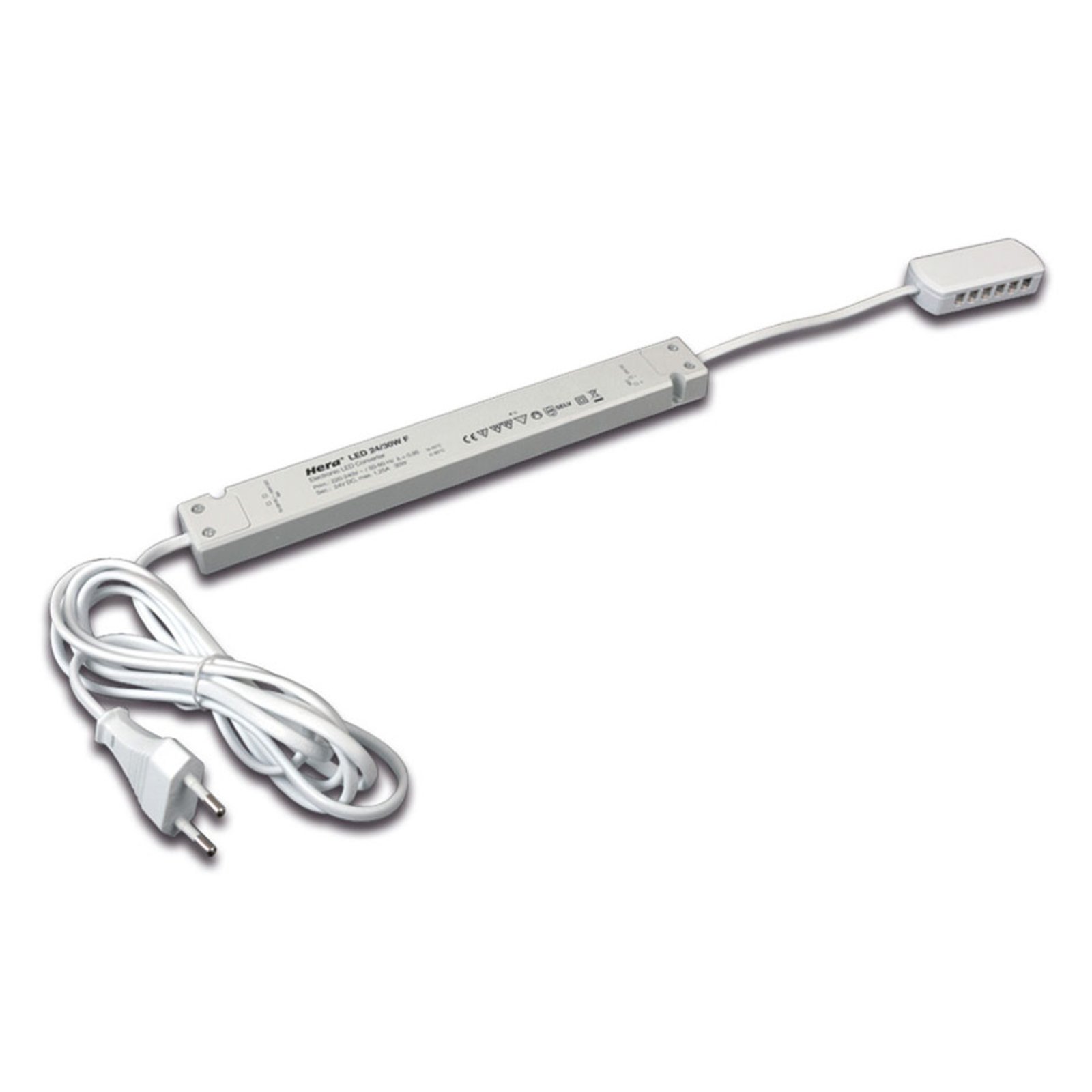
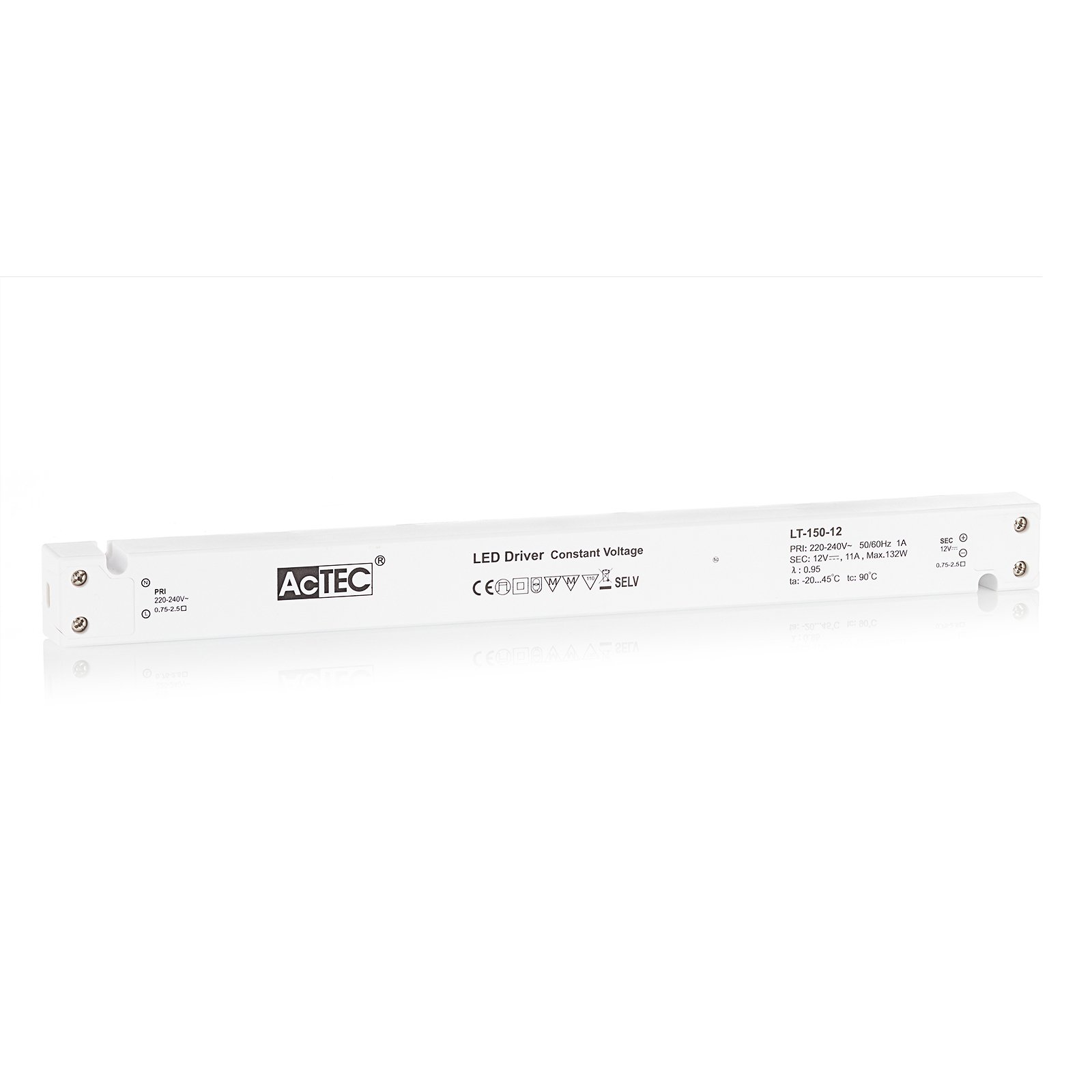
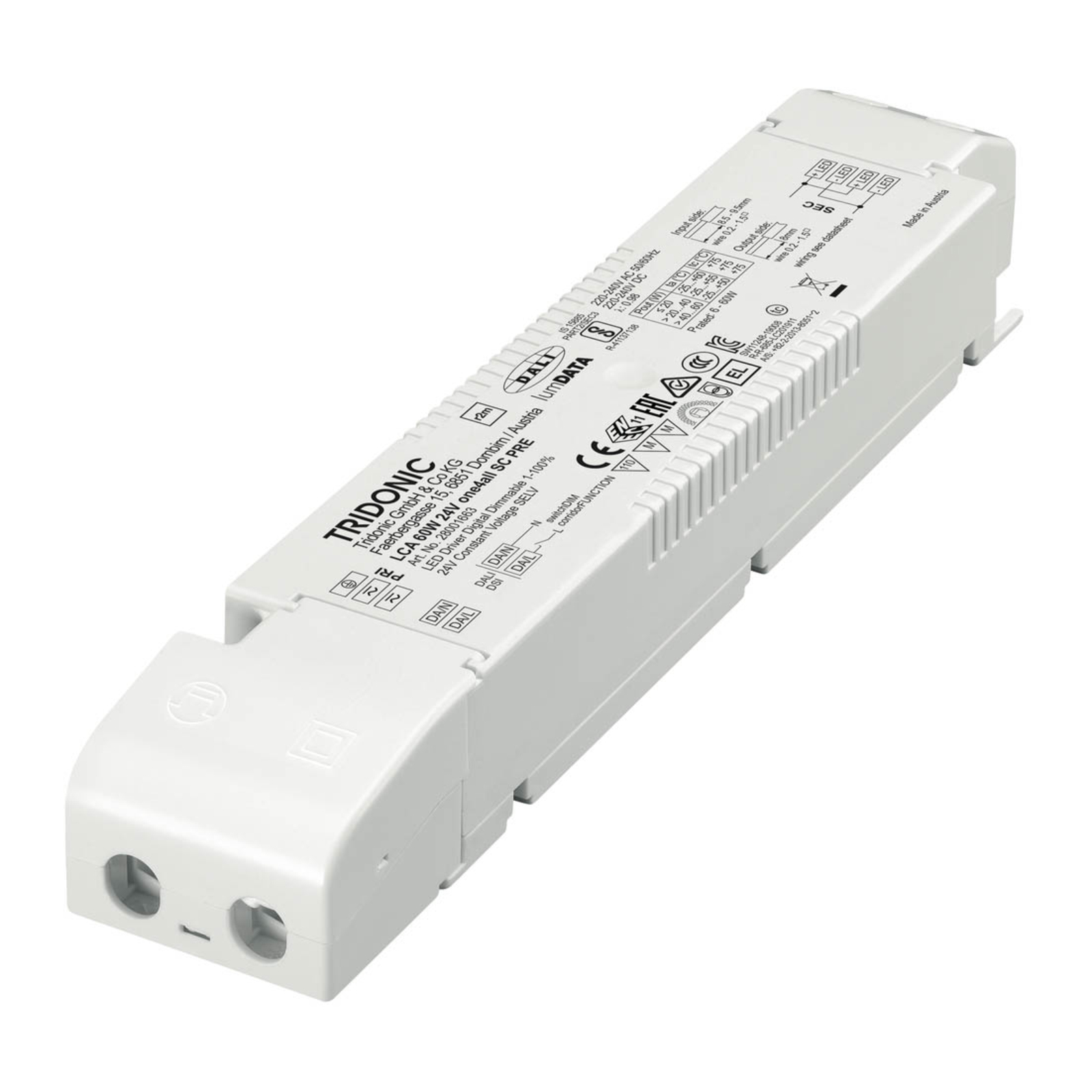
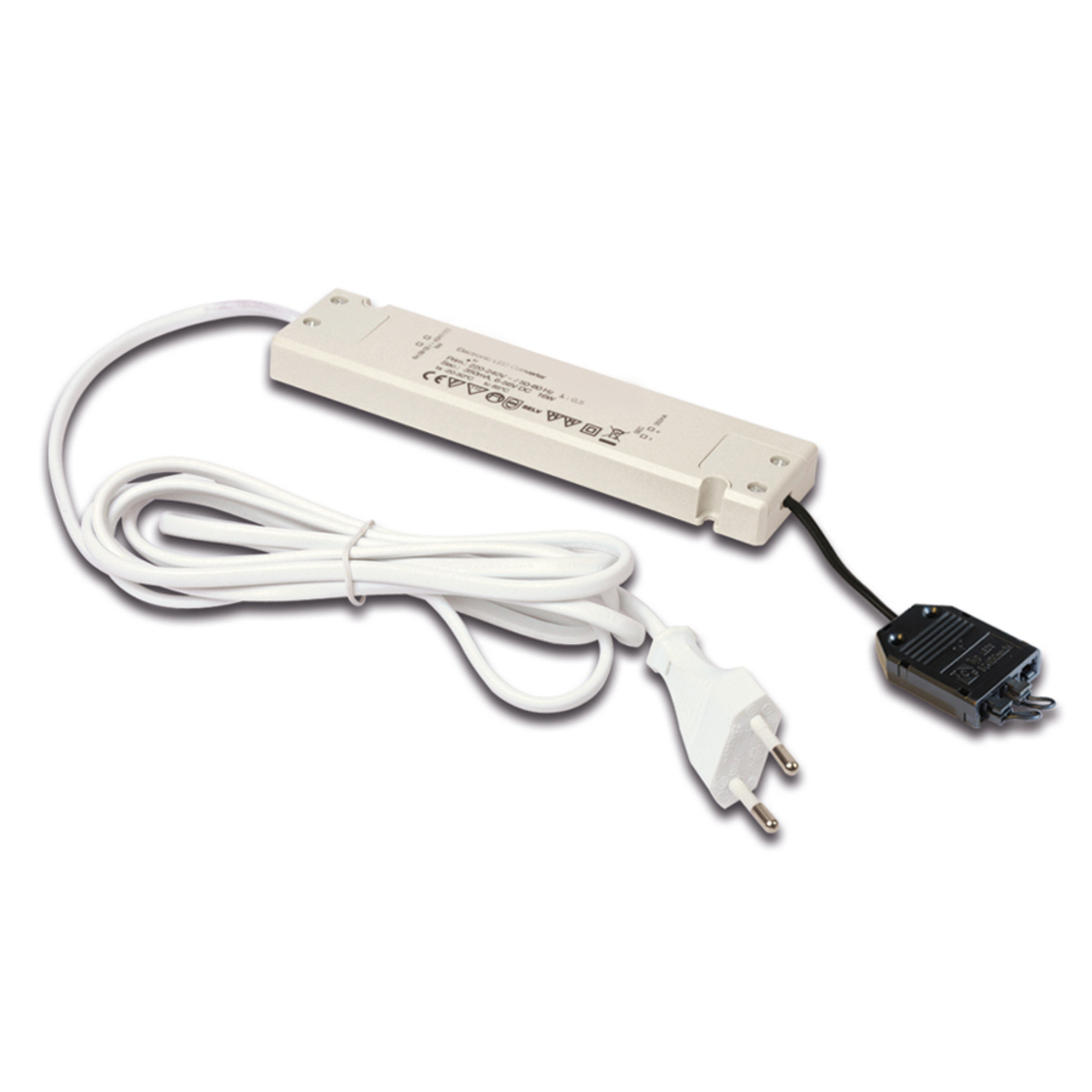
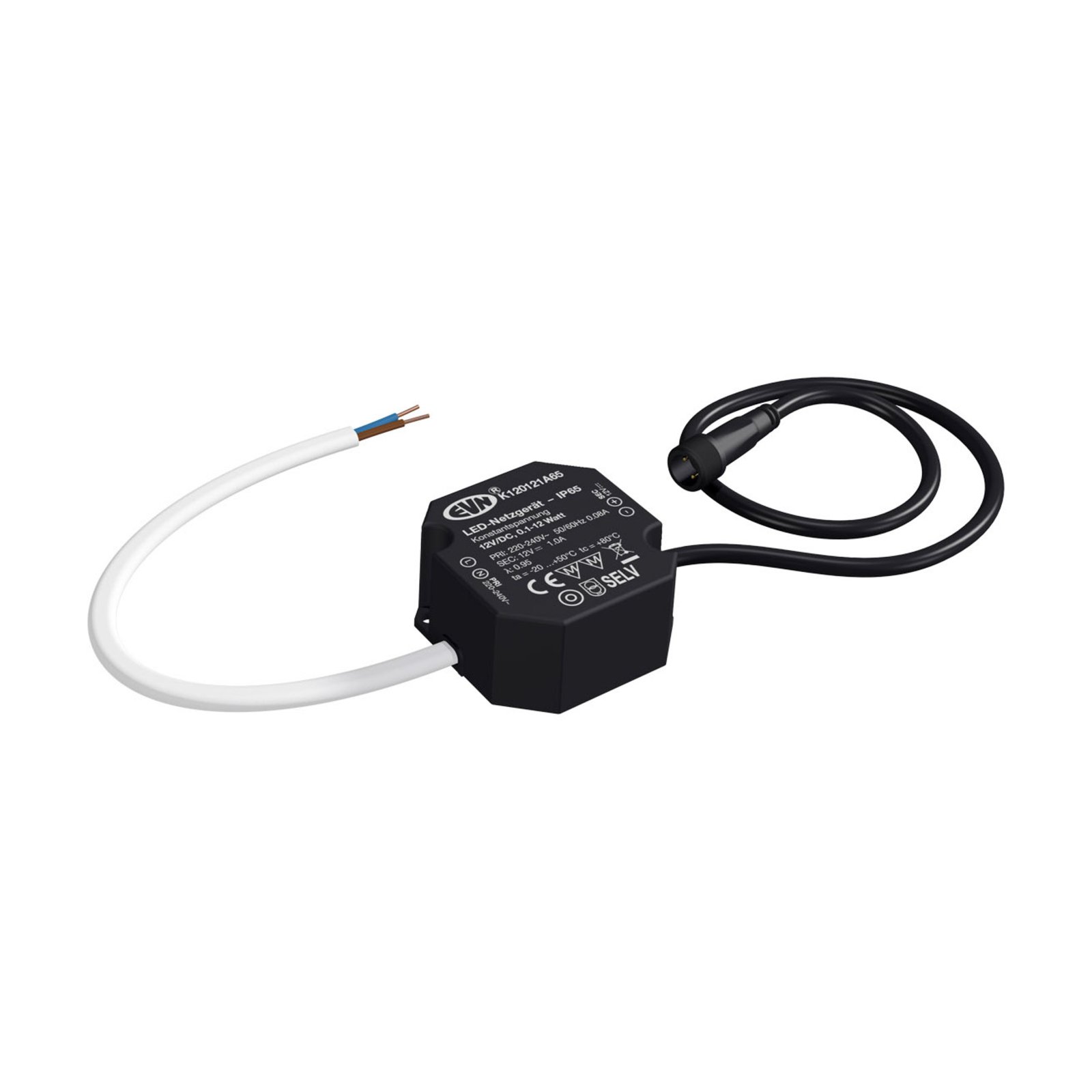
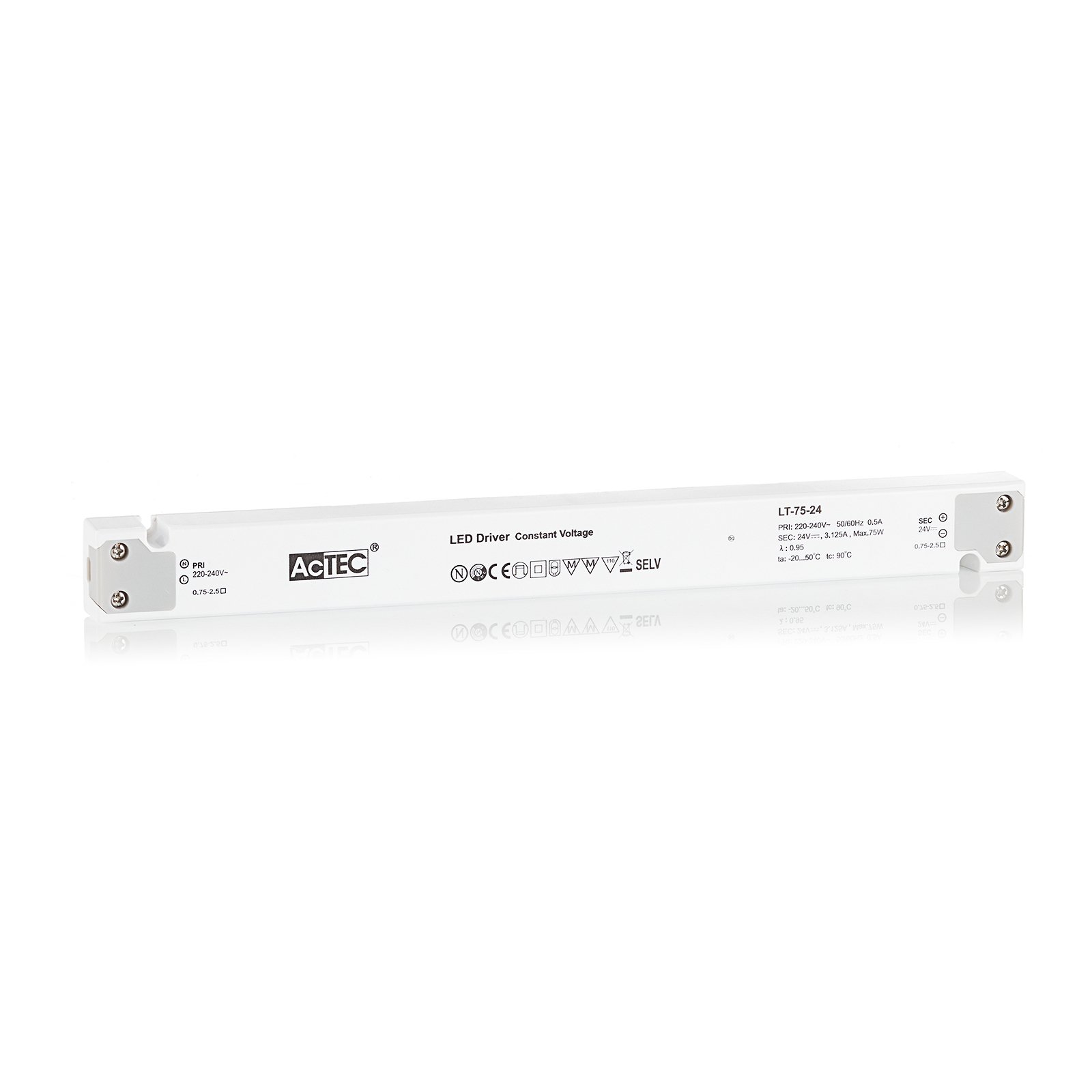
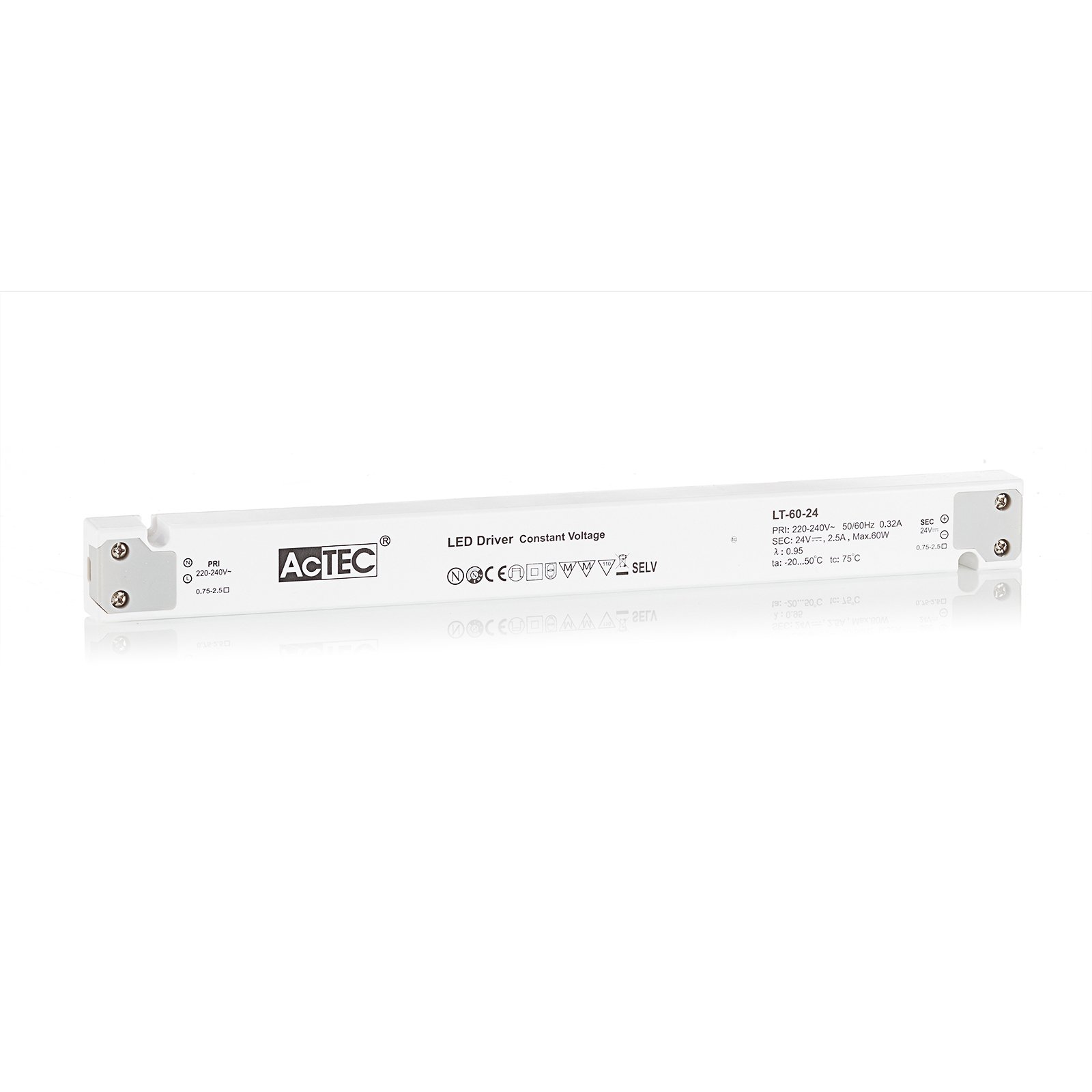
Two types of constant-voltage power supply units
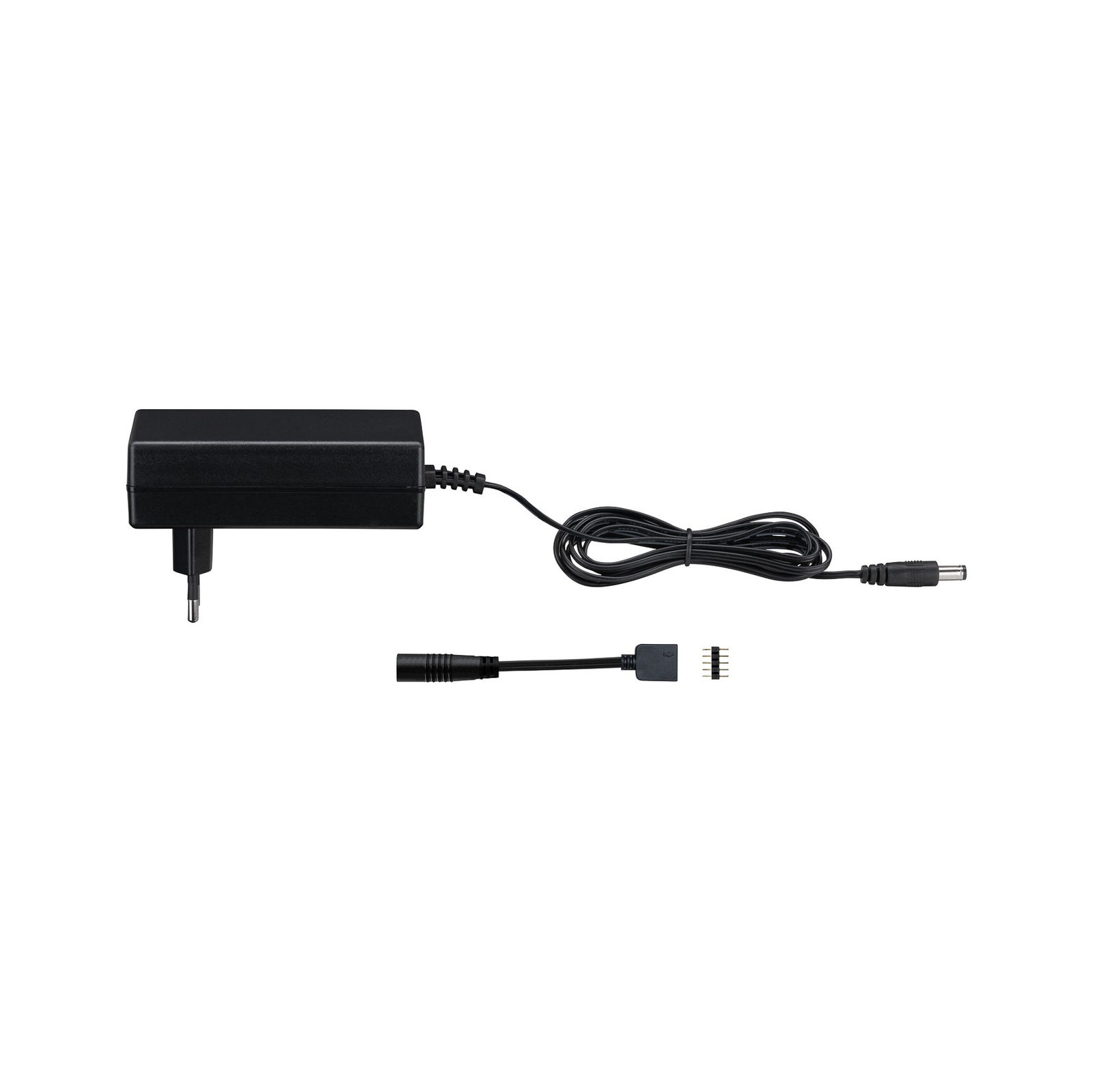
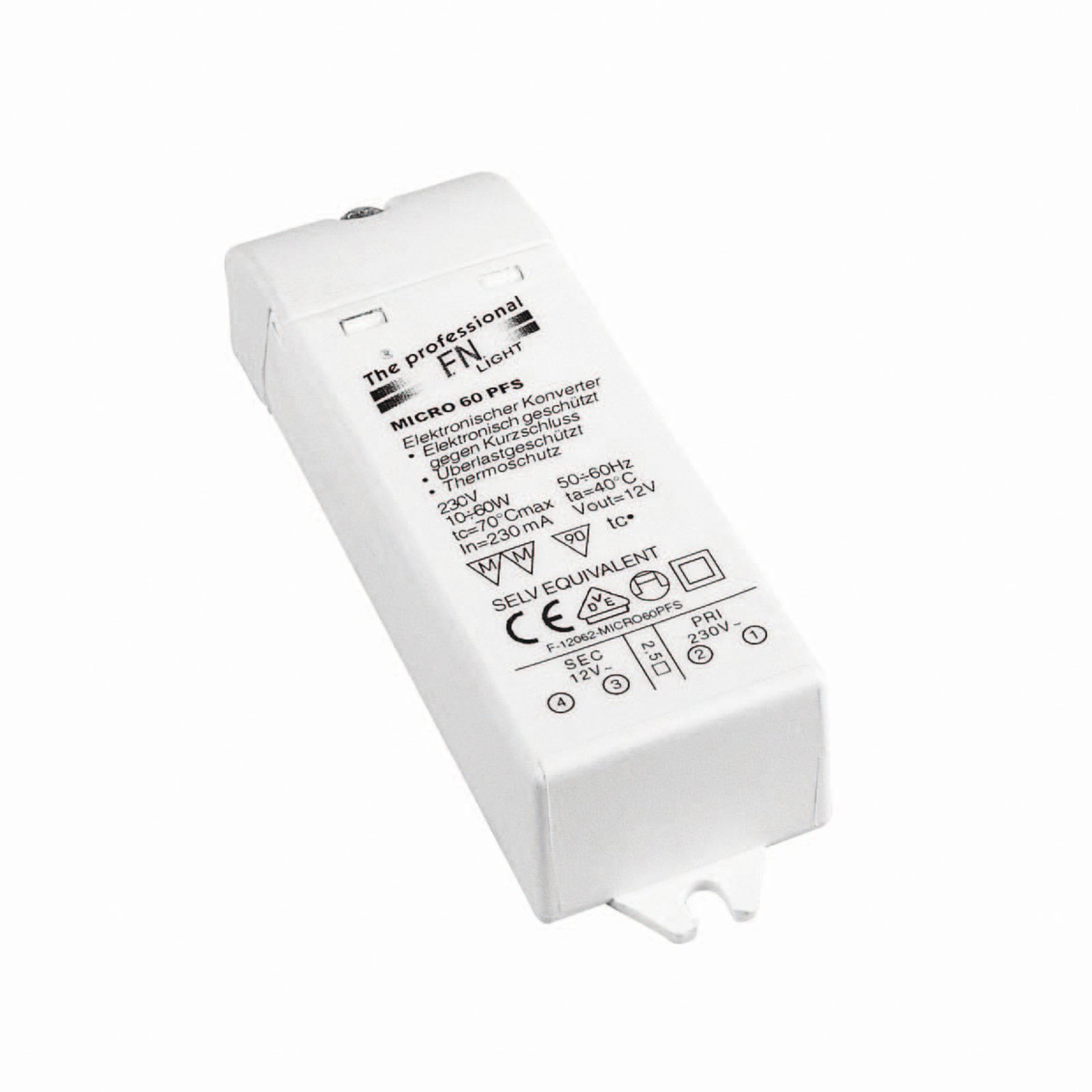
Two different types of transformer can be used to operate lights: the conventional, magnetic transformer (K transformer) or the electronic transformer (E transformer). The conventional transformer is a mechanical transformer whose mode of operation is based on the interplay of two coils and the law of induction. The electronic transformer, on the other hand, converts the voltage using electronic circuits. It has the advantage of being much more compact and lighter than a conventional transformer.
The history of the transformer
Although the induction principle on which the conventional transformer is based had been known since Michael Faraday's discovery in 1831, the first transformer was not developed until 50 years later. In 1851, Lucien Gaulard and John Gibbs presented their invention, the first transformer, in London. Four years later, however, the Hungarian Károly Zipernowsky, Miksa Déri and Otto Titusz Bláthy applied for the patent. From then on, transformers were sold worldwide by a Hungarian company. However, an American by the name of George Westinghouse was to become known for the spread of the alternating current system and thus the transformer.
The strike-through prices correspond to the manufacturer's RRP.
All prices include 20% VAT, delivery costs excluded.